HP 6125G HP 6125G & 6125G/XG Blade Switches Fundamentals Configuration - Page 46
Setting the DSCP value for IP to use for outgoing Telnet packets, Logging in through SSH
 |
View all HP 6125G manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 46 highlights
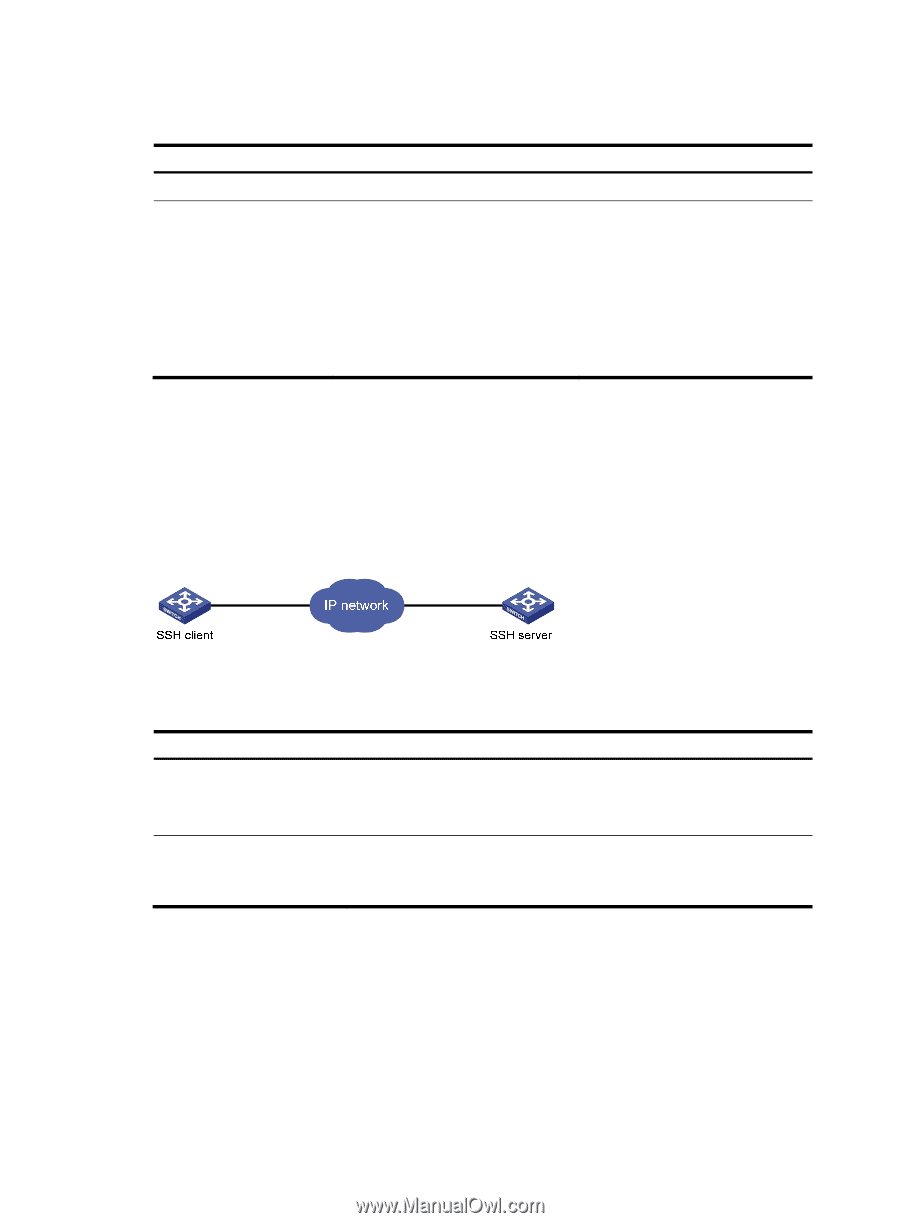
Setting the DSCP value for IP to use for outgoing Telnet packets Step 1. Enter system view. 2. Set the DSCP value for IP to use for outgoing Telnet packets. Command system-view • On a Telnet client running IPv4: telnet client dscp dscp-value • On a Telnet client running IPv6: telnet client ipv6 dscp dscp-value • On a Telnet server running IPv4: telnet server dscp dscp-value • On a Telnet server running IPv6: telnet server ipv6 dscp dscp-value Remarks N/A The default is as follows: • 16 for a Telnet client running IPv4. • 0 for a Telnet client running IPv6. • 48 for a Telnet server running IPv4. • 0 for a Telnet server running IPv6. Logging in through SSH SSH offers a secure approach to remote login. By providing encryption and strong authentication, it protects devices against attacks such as IP spoofing and plaintext password interception. You can log in to the device working as an SSH server for remote management, as shown in Figure 17. You can also use the device as an SSH client to log in to an SSH server. Figure 17 SSH login diagram Table 15 shows the SSH server and client configuration required for a successful SSH login. Table 15 SSH server and client requirements Device role SSH server SSH client Requirements Assign an IP address to a Layer 3 interface, and make sure the interface and the client can reach each other. Configure the authentication mode and other settings. If the host is operating as an SSH client, run the SSH client program on the host. Obtain the IP address of the Layer 3 interface on the server. To control SSH access to the device working as an SSH server, configure authentication and user privilege level for SSH users. By default, password authentication is adopted for SSH login, but no login password is configured. To allow SSH access to the device after you enable the SSH server, you must configure a password. Configuring the SSH server on the device Follow these guidelines when you configure the SSH server: 40