HP 6125G HP 6125G & 6125G/XG Blade Switches Fundamentals Configuration - Page 15
Using the command history function, Viewing history commands
 |
View all HP 6125G manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 15 highlights
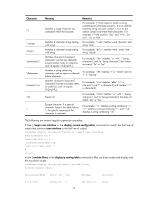
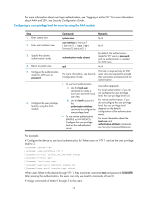
Using the command history function The system can automatically save successfully executed commands to the command history buffer for the current user interface. You can view them and execute them again, or set the maximum number of commands that can be saved in the command history buffer. A command is saved to the command history buffer in the exact format as it was entered. For example, if you enter an incomplete command, the command saved in the command history buffer is also incomplete; if you enter a command by using a command keyword alias, the command saved in the command history buffer also uses the alias. If you enter a command in the same format repeatedly in succession, the system buffers the command only once. If you enter a command repeatedly in different formats, the system buffers each command format. For example, display cu and display current-configuration are buffered as two entries but successive repetitions of display cu create only one entry in the buffer. By default, the command history buffer can save up to 10 commands for each user. To set the capacity of the command history buffer for the current user interface, use the history-command max-size command. Viewing history commands You can use arrow keys to access history commands in Windows 200x and Windows XP Terminal or Telnet. In Windows 9x HyperTerminal, the arrow keys are invalid, and you must use Ctrl+P and Ctrl+N instead. To view command history, use one of the following methods: Task Display all commands in the command history buffer. Display the previous history command. Display the next history command. Command display history-command [ | { begin | exclude | include } regular-expression ] Up arrow key or Ctrl+P Down arrow key or Ctrl+N Setting the command history buffer size for user interfaces Step 1. Enter system view. Command system-view 2. Enter user interface view. user-interface { first-num1 [ last-num1 ] | { aux | vty } first-num2 [ last-num2 ] } 3. Set the maximum number of commands that can be saved in the command history buffer. history-command max-size size-value Remarks N/A N/A Optional. By default, the command history buffer can save up to 10 commands. 9