HP 6125G HP 6125G & 6125G/XG Blade Switches Fundamentals Configuration - Page 84
FTP server configuration example, Network requirements, Configuration procedure,
 |
View all HP 6125G manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 84 highlights
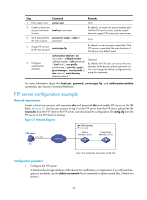
Step Command Remarks 1. Enter system view. system-view N/A 2. Create a local user account and enter local-user user-name its view. By default, no local user account authorized with the FTP service exists, and the system does not support FTP anonymous user access. 3. Set a password for password { simple | cipher } the user account. password N/A 4. Assign FTP service to the user account service-type ftp By default, no service type is specified. If the FTP service is specified, the root directory of the device is by default used. 5. Configure authorization attributes. authorization-attribute { acl acl-number | callback-number callback-number | idle-cut minute | level level | user-profile profile-name | user-role { guest | guest-manager | security-audit } | vlan vlan-id | work-directory directory-name } * Optional. By default, the FTP users can access the root directory of the device, and the user level is 0. You can change the default configuration by using this command. For more information about the local-user, password, service-type ftp, and authorization-attribute commands, see Security Command Reference. FTP server configuration example Network requirements Create a local user account with username abc and password abc and enable FTP server on the IRF fabric in Figure 37. Use the user account to log in to the FTP server from the FTP client, upload the file newest.bin from the FTP client to the FTP server, and download the configuration file config.cfg from the FTP server to the FTP client for backup. Figure 37 Network diagram FTP client 1.2.1.1/16 Internet IRF (FTP server) IP: 1.1.1.1/16 Master (Member_ID=1) Subordinate (Member_ID=2) PC Note: The orange line represents an IRF link. Configuration procedure 1. Configure the FTP server: # Examine the storage medium of the device for insufficiency or impairment. If no sufficient free space is available, use the delete/unreserved file-url command to delete unused files. (Details not shown.) 78