HP 6125G HP 6125G & 6125G/XG Blade Switches Fundamentals Configuration - Page 69
Configuring SNMPv1 or SNMPv2c settings
 |
View all HP 6125G manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 69 highlights
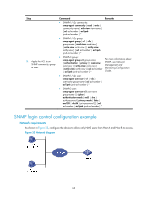
Step 3. Configure an SNMP group and specify its access right. 4. Add a user to the SNMP group. Command snmp-agent group v3 group-name [ authentication | privacy ] [ read-view read-view ] [ write-view write-view ] [ notify-view notify-view ] [ acl acl-number | acl ipv6 ipv6-acl-number ] * snmp-agent usm-user v3 user-name group-name [ [ cipher ] authentication-mode { md5 | sha } auth-password [ privacy-mode { 3des | aes128 | des56 } priv-password ] ] [ acl acl-number | acl ipv6 ipv6-acl-number ] * Remarks By default, no SNMP group is configured. N/A Configuring SNMPv1 or SNMPv2c settings Step 1. Enter system view. Command system-view Remarks N/A 2. Enable the SNMP agent. snmp-agent Optional. By default, the SNMP agent is disabled. You can enable SNMP agent with this command or any command that begins with snmp-agent. 3. Create or update MIB view information. snmp-agent mib-view { excluded | included } view-name oid-tree [ mask mask-value ] Optional. By default, the MIB view name is ViewDefault and OID is 1. 4. Configure SNMP NMS access right. • (Approach 1) Specify the SNMP NMS access right directly by configuring an SNMP community: snmp-agent community { read | write } community-name [ mib-view view-name ] [ acl acl-number | acl ipv6 ipv6-acl-number ] * • (Approach 2) Configure an SNMP group and add a user to the SNMP group: Use either approach. The direct configuration approach is for SNMPv1 or SNMPv2c. The community name configured on the a. snmp-agent group { v1 | v2c } NMS should be consistent group-name [ read-view read-view ] with the username configured [ write-view write-view ] [ notify-view on the agent. notify-view ] [ acl acl-number | acl ipv6 ipv6-acl-number ] * The indirect configuration approach is for SNMPv3. b. snmp-agent usm-user { v1 | v2c } user-name group-name [ acl acl-number | acl ipv6 ipv6-acl-number ] * 63