HP 6125G HP 6125G & 6125G/XG Blade Switches Fundamentals Configuration - Page 19
Configuring user privilege and command levels, Configuring a user privilege level
 |
View all HP 6125G manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 19 highlights
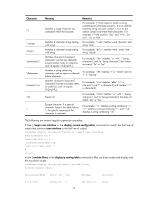
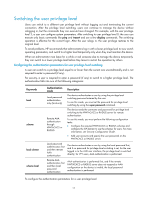
# Use | include Vlan in the display ip routing-table command to filter in route entries that contain Vlan. display ip routing-table | include Vlan Routing Tables: Public Destination/Mask Proto Pre Cost NextHop Interface 192.168.1.0/24 Direct 0 0 192.168.1.42 Vlan999 Configuring user privilege and command levels To avoid unauthorized access, the device defines the user privilege levels and command levels in Table 7. User privilege levels correspond to command levels. A user who has been logged in with a specific privilege level can use only the commands at that level or lower levels. All commands are categorized into four levels: visit, monitor, system, and manage, and are identified from low to high, respectively by 0 through 3. Table 7 Command levels and user privilege levels Level Privilege Default set of commands 0 Visit Includes commands for network diagnosis and commands for accessing an external device. Configuration of commands at this level cannot survive a device restart. Upon device restart, the commands at this level are restored to the default settings. Commands at this level include ping, tracert, telnet and ssh2. Includes commands for system maintenance and service fault diagnosis. Commands at this level are not saved after being configured. After the device is restarted, the commands 1 Monitor at this level are restored to the default settings. Commands at this level include debugging, terminal, refresh, and send. Includes service configuration commands, including routing configuration commands and commands for configuring services at different network levels. 2 System By default, commands at this level include all configuration commands except for those at manage level. Includes commands that influence the basic operation of the system and commands for configuring system support modules. 3 Manage By default, commands at this level involve the configuration commands of file system, FTP, TFTP, Xmodem download, user management, level setting, and parameter settings within a system, which are not defined by any protocols or RFCs. Configuring a user privilege level If the authentication mode on a user interface is scheme, configure a user privilege level for users who access the interface by using the AAA module or directly on the user interface. For SSH users who use public-key authentication, the user privilege level configured directly on the user interface always takes effect. For other users, the user privilege level configured in the AAA module has priority over the one configured directly on the user interface. If the authentication mode on a user interface is none or password, configure the user privilege level directly on the user interface. 13