HP 6125G HP 6125G & 6125G/XG Blade Switches Fundamentals Configuration - Page 87
Configuring TFTP, Prerequisites, Using the device as a TFTP client
 |
View all HP 6125G manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 87 highlights
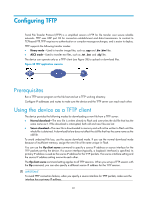
Configuring TFTP Trivial File Transfer Protocol (TFTP) is a simplified version of FTP for file transfer over secure reliable networks. TFTP uses UDP port 69 for connection establishment and data transmission. In contrast to TCP-based FTP, TFTP requires no authentication or complex message exchanges, and is easier to deploy. TFTP supports the following transfer modes: • Binary mode-Used to transfer image files, such as .app and .bin .btw files. • ASCII mode-Used to transfer text files, such as .txt, .bat, and .cfg files. The device can operate only as a TFTP client (see Figure 38) to upload or download files. Figure 38 TFTP application scenario Prerequisites Run a TFTP server program on the file host and set a TFTP working directory. Configure IP addresses and routes to make sure the device and the TFTP server can reach each other. Using the device as a TFTP client The device provides the following modes for downloading a new file from a TFTP server: • Normal download-The new file is written directly to Flash and overwrites the old file that has the same name as it. If file download is interrupted, both old and new files are lost. • Secure download-The new file is downloaded to memory and will not be written to Flash until the whole file is obtained. A download failure does not affect the old file that has the same name as the old file. To avoid undesired file loss, use the secure download mode. If you use the normal download mode because of insufficient memory, assign the new file a file name unique in Flash. You can use the tftp client source command to specify a source IP address or source interface for the TFTP packets sent by the device. If a source interface (typically, a loopback interface) is specified, its primary IP address is used as the source IP address for the TFTP packets. The source interface setting and the source IP address setting overwrite each other. The tftp client source command setting applies to all TFTP sessions. When you set up a TFTP session with the tftp command, you can also specify a different source IP address for the TFTP session. IMPORTANT: To avoid TFTP connection failures, when you specify a source interface for TFTP packets, make sure the interface has a primary IP address. 81