HP 6125G HP 6125G & 6125G/XG Blade Switches Fundamentals Configuration - Page 73
Configuration procedure, Configuring source IP-based SNMP login control
 |
View all HP 6125G manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 73 highlights
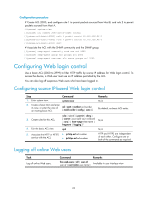
Figure 32 Network diagram Configuration procedure # Configure basic ACL 2000, and configure rule 1 to permit packets sourced from Host B, and rule 2 to permit packets sourced from Host A. system-view [Sysname] acl number 2000 match-order config [Sysname-acl-basic-2000] rule 1 permit source 10.110.100.52 0 [Sysname-acl-basic-2000] rule 2 permit source 10.110.100.46 0 [Sysname-acl-basic-2000] quit # Reference ACL 2000 in user interface view to allow Telnet users from Host A and Host B to access the Device. [Sysname] user-interface vty 0 7 [Sysname-ui-vty0-7] acl 2000 inbound Configuring source IP-based SNMP login control Use a basic ACL (2000 to 2999) to control SNMP logins by source IP address. To access the requested MIB view, an NMS must use a source IP address permitted by the ACL. Configuration procedure To configure source IP-based SNMP login control: Step 1. Enter system view. 2. Create a basic ACL and enter its view, or enter the view of an existing basic ACL. Command system-view Remarks N/A acl [ ipv6 ] number acl-number [ name name ] By default, no basic ACL [ match-order { config | auto } ] exists. 3. Create an ACL rule. 4. Exit the basic ACL view. rule [ rule-id ] { permit | deny } [ source { sour-addr sour-wildcard | any } | time-range time-name | fragment | logging ]* quit N/A N/A 67