HP StorageWorks 1606 Brocade Fabric Watch Administrator's Guide v6.3.0 (53-100 - Page 37
Areas, Environment class areas, Fabric class areas
 |
View all HP StorageWorks 1606 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 37 highlights
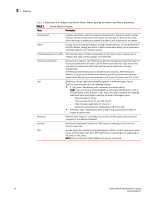
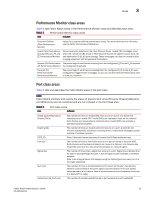
Areas Areas 3 While classes represent large groupings of information, areas represent the information that Fabric Watch monitors. For example, switch temperature, one of the values tracked by Fabric Watch, is an area within the class Environment. The tables in this section describe all of the areas monitored by Fabric Watch, organized by their associated classes. Environment class areas Table 2 lists and describes the Fabric Watch areas in the Environment class. TABLE 2 Environment class areas Area Description Power Supply Temperature Monitors whether power supplies within the switch are on, off, present, absent, or faulty. Fabric Watch monitors power supplies to be sure that power is always available to a switch. Refers to the ambient temperature inside the switch, in degrees Celsius. Temperature sensors monitor the switch in case the temperature rises to levels at which damage to the switch might occur. NOTE Event Manager (EM) now manages fan monitoring; switch status is calculated based on fan status reported by EM. You can use the fanShow command to view the fan status. Fabric class areas Table 3 lists Fabric Watch areas in the Fabric class and describes each area. TABLE 3 Fabric class areas Area Description Domain ID Changes Monitors forced domain ID changes. Forced domain ID changes occur when there is a conflict of domain IDs in a single fabric and the principal switch has to assign another domain ID to a switch. Fabric logins Activates when ports and devices initialize with the fabric. Fabric reconfigure E_Port downs Tracks the number of reconfigurations of the fabric. Fabric reconfiguration occurs when: • Two fabrics with the same domain ID are connected. • Two fabrics are joined. • An E_Port or VE_Port goes offline. • A principal link segments from the fabric. Tracks the number of times that an E_Port or VE_Port goes down. E_Ports and VE_Ports go down each time you remove a cable or an SFP (where there are SFP failures or transient errors). Fabric Watch Administrator's Guide 13 53-1001342-01