HP Superdome SX2000 User Service Guide, Seventh Edition - HP Integrity Superdo - Page 17
Overview, Server History and Specifications - integrity server
 |
View all HP Superdome SX2000 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 17 highlights
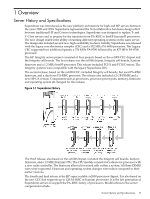
1 Overview Server History and Specifications Superdome was introduced as the new platform architecture for high-end HP servers between the years 2000 and 2004. Superdome represented the first collaborative hardware design effort between traditional HP and Convex technologies. Superdome was designed to replace T- and V-Class servers and to prepare for the transition from PA-RISC to Intel® Itanium® processors. The new design enabled the ability of running different operating systems on the same server. The design also included several new, high-availability features. Initially, Superdome was released with the legacy core electronics complex (CEC) and a 552 MHz PA-8600 processor. The Legacy CEC supported two additional speeds; a 750 MHz PA-8700 followed by an 875 MHz PA-8700 processor. The HP Integrity server project consisted of four projects based on the sx1000 CEC chipset and the Integrity cell boards. The first release was the sx1000 chipset, Integrity cell boards, Itanium firmware and a 1.2 MHz Intel® processor. This release included PCI-X and PCI I/O mixes. The Integrity systems were compatible with the legacy Superdome IOX. The second release, based on the sx1000 CEC, included Integrity cell boards, but used PA-RISC firmware, and a dual-core PA-RISC processor. The release also included a 2 GB DIMM and a new HP-UX version. Components such as processors, processor power pods, memory, firmware, and operating system all changed for this release. Figure 1-1 Superdome History The third release, also based on the sx1000 chipset, included the Integrity cell boards, Itanium firmware, and a 1.5 MHz Itanium CPU. The CPU module consisted of a dual-core processor with a new cache controller. The firmware allowed for mixed cells within a system. All three DIMM sizes were supported. Firmware and operating system changes were minor compared to their earlier versions. The fourth and final release is the HP super scalable sx2000 processor chipset. It is also based on the new CEC that supports up to 128 PA-RISC or Itanium processors. It is the last generation of Superdome servers to support the PA-RISC family of processors. Modifications to the server components include: Server History and Specifications 17