HP Superdome SX2000 User Service Guide, Seventh Edition - HP Integrity Superdo - Page 26
Backplane, Crossbar Chip
 |
View all HP Superdome SX2000 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 26 highlights
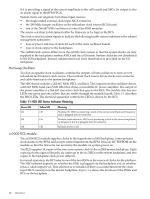
Figure 1-5 HUCB Backplane The system backplane assembly fabric provides the following functionality in an sx2000 system: • Interfaces the CLU subsystem to the system backplane and cell modules • Houses the system crossbar switch fabrics and cell modules • Provides switch fabric interconnect between multiple cabinets • Generates system clock sources • Performs redundant system clock source switching • Distributes the system clock to crossbar chips and cell modules • Distributes HKP to cell modules • Terminates I/O cables to cell modules The backplane supports up to eight cells, interconnected by the crossbar links. A sustained total bandwidth of 25.5 GB is provided to each cell. Each cell connects to three individual XBC ASICs. This connection enables a single chip crossing when a cell communicates with another cell in its four-cell group. When transferring data between cells in different groups, two crossbar links compensate for the resultant multiple chip crossings. This topology also provides for switch fabric redundancy Dual rack/backplane systems contain two identical backplanes. These backplanes use 12 high-speed interface cables as interconnects instead of the flex cable interface previously employed for the legacy Superdome crossbar. The sustainable bisection bandwidth between cabinets is 72 GB/s at a link speed of 2.1 GT/s. Crossbar Chip The crossbar fabrics in the sx2000 are implemented using the XBC crossbar chip. Each XBC is a non-bit-sliced, eight-port non-blocking crossbar that can communicate with the CC or XBC ASICs. Each of the eight ports is full duplex, capable of transmitting and receiving independent packets simultaneously. Each port consists of 20 channels of IBM's HSS technology. Eighteen channels are used for packet data. One channel is used for horizontal link parity, and one channel is a spare. The HSS channels can run from 2.0- 3.2 GT/s. At 3.0 GT/s, each port provides 8.5 GB/s of sustainable bidirectional data bandwidth. Like the CC and the SBA, XBC implements link-level retry to recover from intermittent link errors. XBC can also replace a hard-failed channel with the spare channel during the retry process, which guarantees continued reliable operation in the event of a broken channel, or single or multibit intermittent errors. XBC supports enhanced security between hard partitions by providing write protection on key CSRs. Without protection, CSRs such as the routing tables can be modified by a rogue OS, causing other hard partitions in the system to crash. To prevent this, key CSRs in XBC can only be modified by packets with the Secure bit set. This bit is set by the CC, based on a register that is set only by 26 Overview