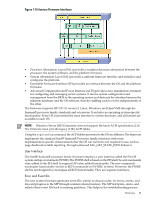
HP Superdome SX2000 User Service Guide, Seventh Edition - HP Integrity Superdo - Page 48
Server Errors, GB memory per cell with 256 MB SDRAMs 1 GB DIMMs
 |
View all HP Superdome SX2000 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 48 highlights
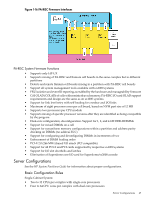
• Minimum of one cell • Maximum of eight cells Dual-Cabinet System: • Six to 64 CPU cores per complex with single-core processors • Twelve to 128 CPU cores per complex with dual-core processors • Minimum of three cells • Maximum of 16 cells • No master/checker support for dual-core processors The rules for mixing processors are as follows: • No mixing of frequencies on a cell or within a partition • No mixing of cache sizes on a cell or within a partition • No mixing of major steppings on a cell or within a partition • Support for Itanium and PA-RISC processors within the same complex, but not in the same partition • Maximum of 32 DIMMs per cell • 32 GB memory per cell with 256 MB SDRAMs (1 GB DIMMs) • 64 GB memory per cell with 512 MB SDRAMs (2 GB DIMMs) • DIMM mixing is allowed Server Errors To support high availability (HA), the new chipset includes functionality for error correction, detection and recovery. Errors in the new chipset are divided into the following categories: • nPartition access • Hardware correctable • Global shared memory • Hardware uncorrectable • Fatal blocking time-out • Deadlock recovery errors These categories are listed in increasing severity, ranging from hardware partition access errors, which are caused by software or hardware running in another partition, to deadlock recovery errors, which indicate a serious hardware failure that requires a reset of the cell to recover. The term software refers to privileged code, such as PDC or the OS, but not to user code. The sx2000 chipset supports the nPartition concept, where user and software errors in one nPartition cannot affect another nPartition. 48 Overview