HP Superdome SX2000 User Service Guide, Seventh Edition - HP Integrity Superdo - Page 30
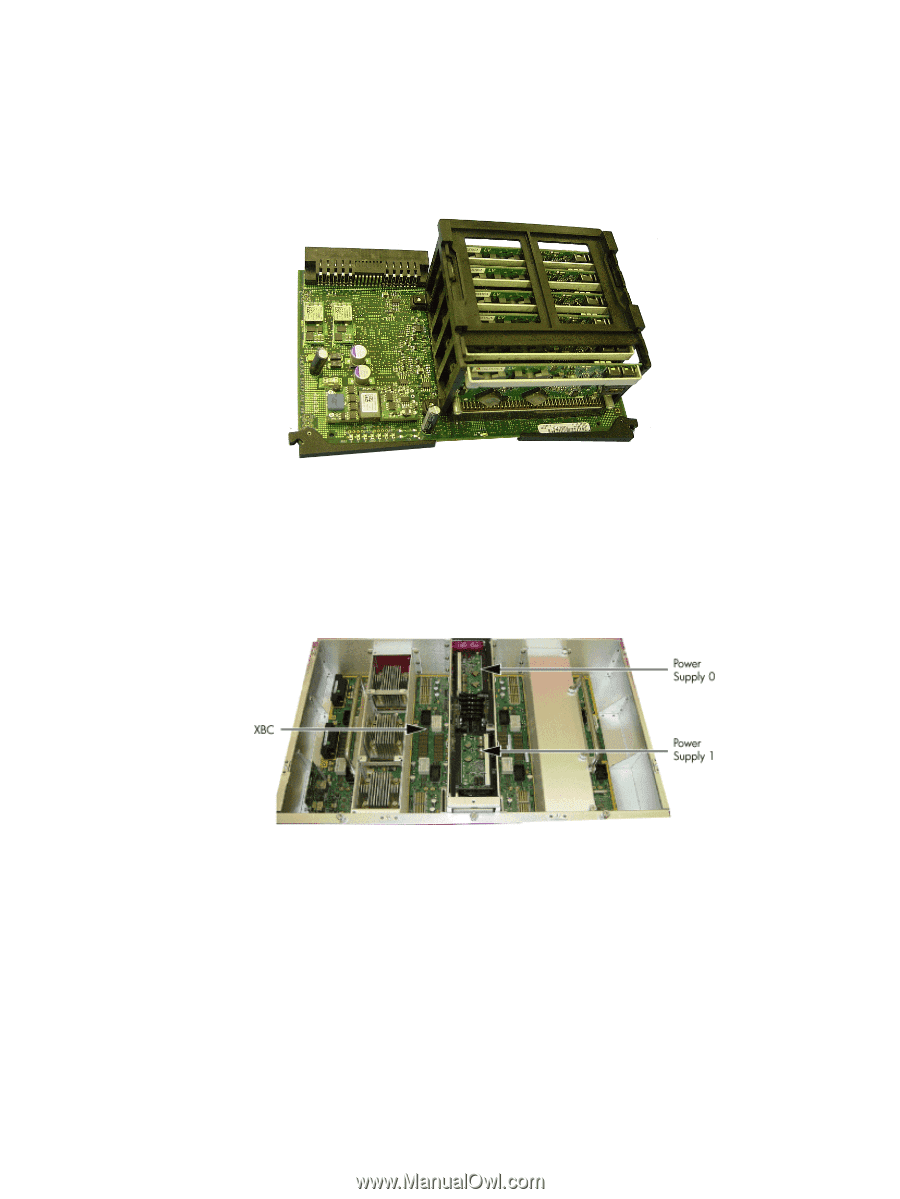
CPUs and Memories, Backplane Power Supply Module, Backplane Rear View
 |
View all HP Superdome SX2000 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 30 highlights
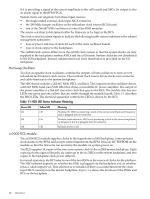
The backplane has two slots for power supply modules. The power supply connector for each slot has a 1-bit slot address to identify the slot. The address bit for power supply slot 0 is grounded. The address bit for slot 1 floats on the backplane. The power supply module provides a pull-up resistor on the address line on slot 1. The power supply module uses the slot address bit as bit A0 for generating a unique I2C address for the FRU ID prom. Figures 1-7 and 1-8 identify and show the location of the backplane power supply modules. Figure 1-7 Backplane Power Supply Module Each power supply slot has a power supply detect bit that determines if the power supply module is inserted into the backplane slot. This bit is routed to an input on the RPMs. The RPM provides a pull-up resistor for logic 1 when the power supply module is missing. When the power supply module is inserted into the slot, the bit is grounded by the power supply and logic 0 is detected by the RPM, indicating that the power supply module is present in the backplane slot. Figure 1-8 Backplane (Rear View) CPUs and Memories The cell provides the processing and memory resources required by each sx2000 system configuration. Each cell includes the following components: four processor module sockets, a single cell (or coherency) controller ASIC, a high-speed crossbar interface, a high-speed I/O interface, eight memory controller ASICs, capacity for up to 32 double-data rate (DDR) DIMMs, high-speed clock distribution circuitry, a management subsystem interface, scan (JTAG) circuitry for manufacturing test, and a low-voltage DC power interface. Figure 1-9 shows the locations of the major components. 30 Overview