Dell EqualLogic PS6210XS EqualLogic Host Integration Tools for Linux Version 1 - Page 34
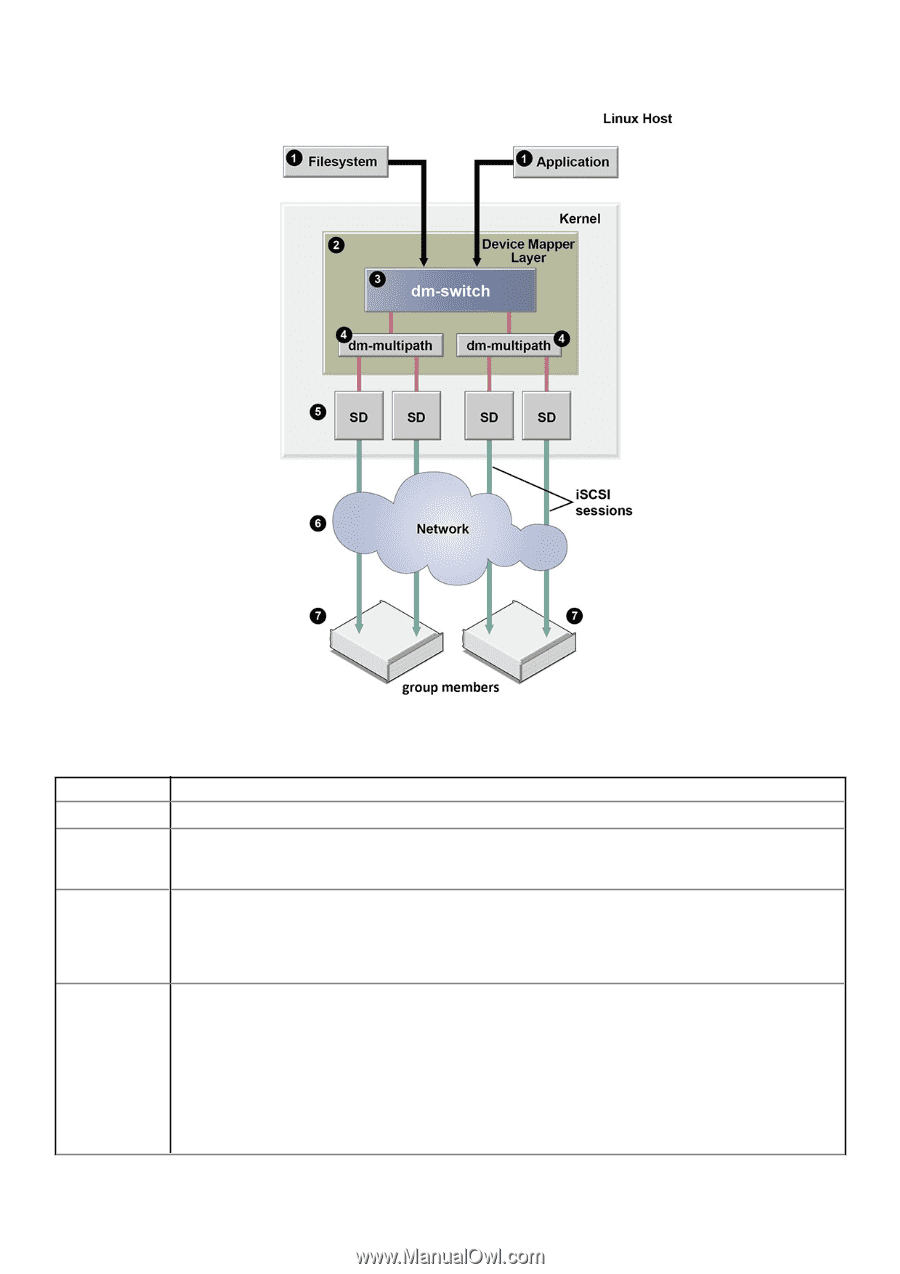
Dell EqualLogic Multipath Device Configuration - Logical View
 |
View all Dell EqualLogic PS6210XS manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 34 highlights
Figure 1. Dell EqualLogic Multipath Device Configuration - Logical View Table 11. Callouts in Figure 1 Callout Number Description of Feature 1 Host file system or application using a block device 2 Device Mapper layer-The Device Mapper allows layering block devices to set up a multipath configuration. HIT/ Linux uses the Device Mapper to build a two-tier device structure with multiple multipath devices (dm- multipath) for each volume and a Device Mapper switch target on top of the multipath devices. 3 Switch device (one per volume)-The ehcmd daemon builds a single top-tier switch device for each volume the host system logs in to with the dm-switch device. The dm-switch device determines on which group the I/O data resides, routes I/O to the appropriate multipath device and thereby to the appropriate member based on the starting logical block number of the I/O. Because this device is not a multipath device, the standard multipath command line tools do not report it. 4 Multiple dm-multipath devices are built for each volume that the host uses, one for each group member that holds a portion of the volume. Each of the dm-multipath devices lists all SD devices, some in a preferred priority group and some in a non-preferred group. The SD block devices that represent direct paths to that member are placed in a preferred priority group and are used for all I/O in normal conditions; all other SD devices are put in a nonpreferred priority group so they are available for failover of I/O. The ehcmd daemon builds and maintains this configuration, responds to any changes in SAN topology, such as device addition or device removal, and modifies the Device Mapper devices as necessary. Based on load factors, the dm-multipath device determines which iSCSI path should be taken to the group member from the multiple paths in the preferred priority group. When available, the dm-multipath devices use a 34 Configuring Multipath I/O Devices