Netgear FVS318G FVS318G User Manual - Page 160
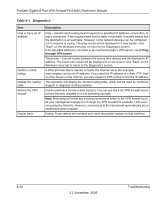
Table 8-1., Diagnostics, Troubleshooting
 |
UPC - 606449064827
View all Netgear FVS318G manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 160 highlights
ProSafe Gigabit 8 Port VPN Firewall FVS318G Reference Manual Table 8-1. Diagnostics Item Ping or trace an IP address Perform a DNS lookup Display the routing table Reboot the VPN firewall Packet trace Description Ping - Used to send a ping packet request to a specified IP address-most often, to test a connection. If the request times out (no reply is received), it usually means that the destination is unreachable. However, some network devices can be configured not to respond to a ping. The ping results will be displayed in a new screen; click "Back" on the Windows menu bar to return to the Diagnostics screen. If the specified address is intended to be reached through a VPN tunnel, check Ping through VPN tunnel. Traceroute - Lists all routers between the source (this device) and the destination IP address. The traceroute results will be displayed in a new screen; click "Back" on the Windows menu bar to return to the Diagnostics screen. A DNS (Domain Name Server) converts the Internet name (for example, www.netgear.com) to an IP address. If you need the IP address of a Web, FTP, Mail or other Server on the Internet, you can request a DNS lookup to find the IP address. This operation will display the internal routing table, which can be used by Technical Support to diagnose routing problems. Used to perform a remote reboot (restart). You can use this if the VPN firewall seems to have become unstable or is not operating normally. Note: Rebooting will break any existing connections either to the VPN firewall (such as your management session) or through the VPN firewall (for example, LAN users accessing the Internet). However, connections to the Internet will automatically be reestablished when possible. Packet Trace selects the interface and starts the packet capture on that interface. 8-10 1.1 November, 2009 Troubleshooting