Netgear FVS318G FVS318G User Manual - Page 79
Configuring Port Triggering, Add IP/MAC Bindings, MAC Address, Set Poll Interval, Apply - port forward
 |
UPC - 606449064827
View all Netgear FVS318G manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 79 highlights
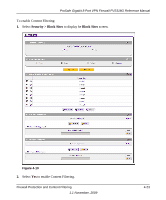
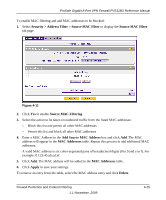
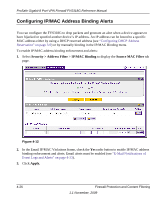
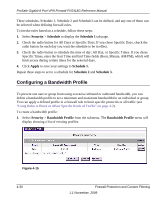
ProSafe Gigabit 8 Port VPN Firewall FVS318G Reference Manual 4. To add a manual binding entry, enter the following data in the Add IP/MAC Bindings section: a. Enter a Name for the bound host device. b. Enter the MAC Address and IP Address to be bound. A valid MAC address is six colonseparated pairs of hexadecimal digits (0 to 9 and a to f). For example: 01:23:45:ab:cd:ef. c. From the pull-down list, select whether dropped packets should be logged to a special counter. To view the counter, click the Set Poll Interval link at the top of the menu. 5. Click Apply. The specified binding will be added to the list. Configuring Port Triggering Port triggering allows some applications to function correctly that would otherwise be partially blocked by the firewall when the router is in NAT mode. Some applications require that when external devices connect to them, they receive data on a specific port or range of ports. The router must send all incoming data for that application only on the required port or range of ports. Using this feature requires that you know the port numbers used by the application. Port triggering allows computers on the private network (LAN) to request that one or more ports be forwarded to them. Unlike basic port forwarding which forwards ports to only one preconfigured IP address, port triggering waits for an outbound request from the private network on one of the defined outgoing ports. It then automatically sets up forwarding to the IP address that sent the request. When the application ceases to transmit data over the port, the router waits for a timeout interval and then closes the port or range of ports, making them available to other computers on the private network. Once configured, port triggering operates as follows: 1. A PC makes an outgoing connection using a port number defined in the Port Triggering table. 2. The VPN firewall records this connection, opens the additional incoming port or ports associated with this entry in the Port Triggering table, and associates them with the PC. 3. The remote system receives the PC's request and responds using the different port numbers that you have now opened. 4. The VPN firewall router matches the response to the previous request, and forwards the response to the PC. Without Port Triggering, this response would be treated as a new connection request rather than a response. As such, it would be handled in accordance with the inbound service rules. Firewall Protection and Content Filtering 1.1 November, 2009 4-27