HP 6125G HP 6125G & 6125G/XG Blade Switches Layer 3 - IP Services Conf - Page 114
DHCPv6 overview, Introduction to DHCPv6, DHCPv6 address/prefix assignment
 |
View all HP 6125G manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 114 highlights
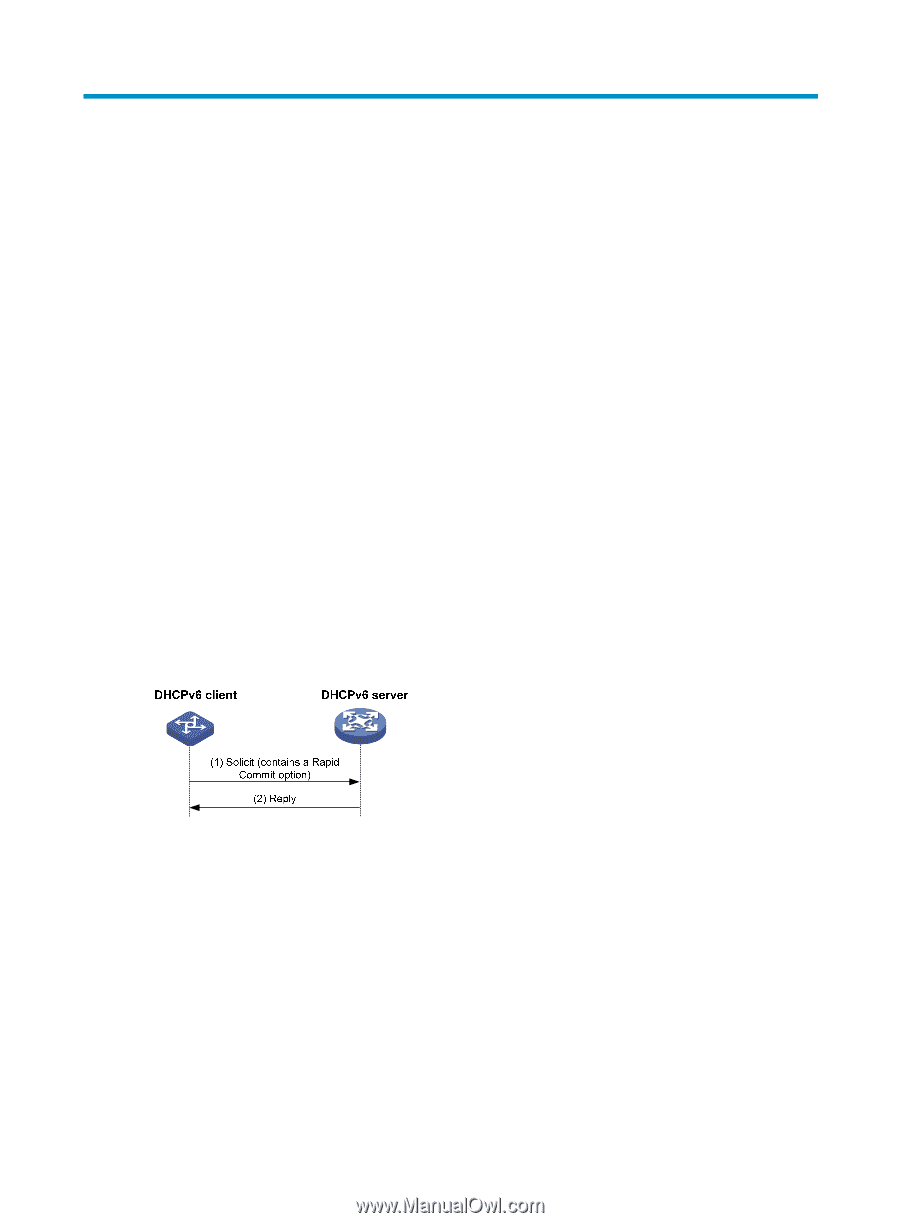
DHCPv6 overview Introduction to DHCPv6 The Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol for IPv6 (DHCPv6) was designed based on IPv6 addressing scheme and is used for assigning IPv6 prefixes, IPv6 addresses and other configuration parameters to hosts. Compared with other IPv6 address allocation methods (such as manual configuration and stateless address autoconfiguration), DHCPv6 can: • Record addresses assigned to hosts and assign specific addresses to hosts, thus facilitating network management. • Assign prefixes to devices, facilitating automatic configuration and management of the entire network. • Assign other configuration parameters, such as DNS server addresses and domain names. DHCPv6 address/prefix assignment A process of DHCPv6 address/prefix assignment involves two or four messages. The following describe the detailed processes. Rapid assignment involving two messages Figure 49 Rapid assignment involving two messages As shown in Figure 49, the rapid assignment involving two messages operates in the following steps. 1. The DHCPv6 client sends out a Solicit message that contains a Rapid Commit option, requesting that rapid assignment of address/prefix and other configuration parameters should be preferred. 2. If the DHCPv6 server supports rapid assignment, it responds with a Reply message containing the assigned IPv6 address/prefix and other configuration parameters. If the DHCPv6 server does not support rapid assignment, Assignment involving four messages is implemented. Assignment involving four messages Figure 50 shows the process of IPv6 address/prefix assignment involving four messages. 106