HP 6125G HP 6125G & 6125G/XG Blade Switches Layer 3 - IP Services Conf - Page 29
Assigning an IP address to an interface, Configuration guidelines, Configuration procedure
 |
View all HP 6125G manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 29 highlights
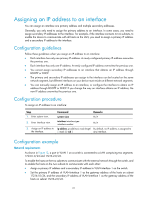
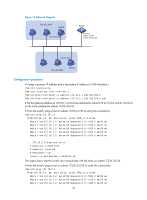
Assigning an IP address to an interface You can assign an interface one primary address and multiple secondary addresses. Generally, you only need to assign the primary address to an interface. In some cases, you need to assign secondary IP addresses to the interface. For example, if the interface connects to two subnets, to enable the device to communicate with all hosts on the LAN, you need to assign a primary IP address and a secondary IP address to the interface. Configuration guidelines Follow these guidelines when you assign an IP address to an interface: • Each interface has only one primary IP address. A newly configured primary IP address overwrites the previous one. • Each interface has only one IP address. A newly configured IP address overwrites the previous one. • You cannot assign secondary IP addresses to an interface that obtains an IP address through BOOTP or DHCP. • The primary and secondary IP addresses you assign to the interface can be located on the same network segment, but different interfaces on your device must reside on different network segments. • You can manually assign an IP address to an interface, or configure the interface to obtain an IP address through BOOTP or DHCP. If you change the way an interface obtains an IP address, the new IP address overwrites the previous one. Configuration procedure To assign an IP address to an interface: Step 1. Enter system view. 2. Enter interface view. 3. Assign an IP address to the interface. Command Remarks system-view N/A interface interface-type interface-number N/A ip address ip-address { mask-length By default, no IP address is assigned to | mask } [ sub ] any interface. Configuration example Network requirements As shown in Figure 13, a port in VLAN 1 on a switch is connected to a LAN comprising two segments: 172.16.1.0/24 and 172.16.2.0/24. To enable the hosts on the two subnets to communicate with the external network through the switch, and to enable the hosts on the two subnets to communicate with each other: • Assign a primary IP address and a secondary IP address to VLAN-interface 1 on the switch. • Set the primary IP address of VLAN-interface 1 as the gateway address of the hosts on subnet 172.16.1.0/24, and the secondary IP address of VLAN-interface 1 as the gateway address of the hosts on subnet 172.16.2.0/24. 21