HP 6125G HP 6125G & 6125G/XG Blade Switches Layer 3 - IP Services Conf - Page 22
Proxy ARP configuration examples, Network requirements, Configuration procedure
 |
View all HP 6125G manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 22 highlights
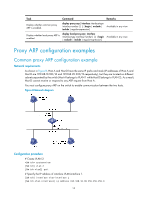
Task Command Remarks Display whether common proxy ARP is enabled. display proxy-arp [ interface interface-type interface-number ] [ | { begin | exclude | include } regular-expression ] Available in any view Display whether local proxy ARP is enabled. display local-proxy-arp [ interface interface-type interface-number ] [ | { begin | exclude | include } regular-expression ] Available in any view Proxy ARP configuration examples Common proxy ARP configuration example Network requirements As shown in Figure 8, Host A and Host D have the same IP prefix and mask (IP addresses of Host A and Host D are 192.168.10.100/16 and 192.168.20.200/16 respectively), but they are located on different subnets separated by the switch (Host A belongs to VLAN 1 while Host D belongs to VLAN 2). As a result, Host D cannot receive or respond to any ARP request from Host A. You must configure proxy ARP on the switch to enable communication between the two hosts. Figure 8 Network diagram Configuration procedure # Create VLAN 2. system-view [Switch] vlan 2 [Switch-vlan2] quit # Specify the IP address of interface VLAN-interface 1. [Switch] interface vlan-interface 1 [Switch-Vlan-interface1] ip address 192.168.10.99 255.255.255.0 14