HP 6125G HP 6125G & 6125G/XG Blade Switches Layer 3 - IP Services Conf - Page 124
Displaying and maintaining the DHCPv6 client, Stateless DHCPv6 configuration example, Network
 |
View all HP 6125G manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 124 highlights
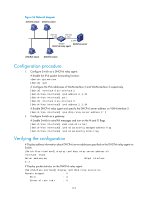
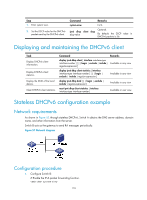
Step 1. Enter system view. 2. Set the DSCP value for the DHCPv6 packets sent by the DHCPv6 client. Command Remarks system-view N/A Optional. ipv6 dhcp client dscp dscp-value By default, the DSCP value in DHCPv6 packets is 56. Displaying and maintaining the DHCPv6 client Task Display DHCPv6 client information. Display DHCPv6 client statistics. Display the DUID of the local device. Clear DHCPv6 client statistics. Command Remarks display ipv6 dhcp client [ interface interface-type interface-number ] [ | { begin | exclude | include } Available in any view regular-expression ] display ipv6 dhcp client statistics [ interface interface-type interface-number ] [ | { begin | exclude | include } regular-expression ] Available in any view display ipv6 dhcp duid [ | { begin | exclude | include } regular-expression ] Available in any view reset ipv6 dhcp client statistics [ interface interface-type interface-number ] Available in user view Stateless DHCPv6 configuration example Network requirements As shown in Figure 57, through stateless DHCPv6, Switch A obtains the DNS server address, domain name, and other information from the server. Switch B acts as the gateway to send RA messages periodically. Figure 57 Network diagram Configuration procedure 1. Configure Switch B: # Enable the IPv6 packet forwarding function. system-view 116