HP 6125G HP 6125G & 6125G/XG Blade Switches Layer 3 - IP Services Conf - Page 63
Enabling DHCP starvation attack protection
 |
View all HP 6125G manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 63 highlights
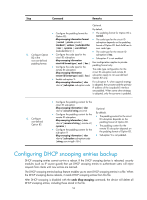
To configure DHCP snooping entries backup: Step 1. Enter system view. Command system-view 2. Specify the name of the file for storing DHCP snooping dhcp-snooping binding entries. database filename filename 3. Back up DHCP snooping entries to the file. dhcp-snooping binding database update now 4. Set the interval at which the DHCP snooping entry file is refreshed. dhcp-snooping binding database update interval minutes Remarks N/A Not specified by default. DHCP snooping entries are stored immediately after this command is used and then updated at the interval set by the dhcp-snooping binding database update interval command. Optional. DHCP snooping entries will be stored to the file each time this command is used. Optional. By default, the file is not refreshed periodically. Enabling DHCP starvation attack protection A DHCP starvation attack occurs when an attacker constantly sends forged DHCP requests using different MAC addresses in the chaddr field to a DHCP server. This exhausts the IP address resources of the DHCP server so legitimate DHCP clients cannot obtain IP addresses. The DHCP server may also fail to work because of exhaustion of system resources. You can protect against starvation attacks in the following ways: • To relieve a DHCP starvation attack that uses DHCP packets encapsulated with different source MAC addresses, you can limit the number of MAC addresses that a Layer 2 port can learn. • To prevent a DHCP starvation attack that uses DHCP requests encapsulated with the same source MAC address, enable MAC address check on the DHCP snooping device. With this function enabled, the DHCP snooping device compares the chaddr field of a received DHCP request with the source MAC address field of the frame. If they are the same, the request is considered valid and forwarded to the DHCP server. If not, the request is discarded. Enable MAC address check only on Layer 2 Ethernet ports and Layer 2 aggregate interfaces. To enable MAC address check: Step 1. Enter system view. 2. Enter interface view. 3. Enable MAC address check. Command system-view interface interface-type interface-number dhcp-snooping check mac-address Remarks N/A N/A Disabled by default 55