HP 6125G HP 6125G & 6125G/XG Blade Switches Layer 3 - IP Services Conf - Page 132
Protocols and standards, Tunneling configuration task list
 |
View all HP 6125G manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 132 highlights
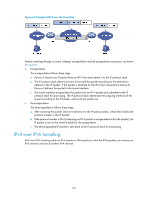
Figure 63 shows the encapsulation and de-encapsulation processes. • Encapsulation a. After receiving the IPv6 packet, the interface of Device A connecting private network A submits it to the IPv6 module for processing. The IPv6 module then determines how to forward the packet. b. If the packet is destined for Host B connected to Device B, the packet is sent to Router A's tunnel interface that is connected to Device B. c. After receiving the packet, the tunnel interface adds an IPv6 header to it and submits it to the IPv6 module for processing. d. The IPv6 module re-determines how to forward the packet according to the destination address in the IPv6 header. • De-encapsulation The de-encapsulation follows these steps: a. The packet received from the IPv6 network interface is sent to the IPv6 module for processing. b. The IPv6 module checks the protocol type of the data portion encapsulated in the IPv6 packet. If the encapsulation protocol is IPv6, the packet is sent to the tunnel processing module for de-encapsulation. c. The de-encapsulated packet is sent to the IPv6 protocol module for the secondary routing process. Protocols and standards • RFC 1853, IP in IP Tunneling • RFC 2473, Generic Packet Tunneling in IPv6 Specification • RFC 2893, Transition Mechanisms for IPv6 Hosts and Routers • RFC 3056, Connection of IPv6 Domains via IPv4 Clouds • RFC 4214, Intra-Site Automatic Tunnel Addressing Protocol (ISATAP) Tunneling configuration task list Task Configuring a tunnel interface Configuring an IPv6 over IPv4 tunnel Configuring an IPv4 over IPv4 tunnel Configuring an IPv4 over IPv6 tunnel Configuring an IPv6 over IPv6 tunnel Configuring an IPv6 manual tunnel Configuring a 6to4 tunnel Configuring an ISATAP tunnel Remarks Required. Optional. Use one as needed. Optional. Optional. Optional. 124