HP 6125G HP 6125G & 6125G/XG Blade Switches Layer 3 - IP Services Conf - Page 31
Configuring IP unnumbered, Overview, Configuration guidelines, Configuration prerequisites
 |
View all HP 6125G manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 31 highlights
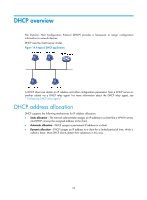
Reply from 172.16.2.2: bytes=56 Sequence=4 ttl=255 time=26 ms Reply from 172.16.2.2: bytes=56 Sequence=5 ttl=255 time=26 ms --- 172.16.2.2 ping statistics --5 packet(s) transmitted 5 packet(s) received 0.00% packet loss round-trip min/avg/max = 25/25/26 ms The output shows that the switch can communicate with the hosts on subnet 172.16.2.0/24. # From a host on subnet 172.16.2.0/24, ping a host on subnet 172.16.1.0/24 to verify the connectivity. Host B can be successfully pinged from Host A. Configuring IP unnumbered Overview Logically, to enable IP on an interface, you must assign this interface a unique IP address. Yet, you can borrow an IP address already configured on one of other interfaces on your device instead. This is called "IP unnumbered" and the interface borrowing the IP address is called "IP unnumbered interface". You can use IP unnumbered to save IP addresses either when available IP addresses are inadequate or when an interface is brought up only for occasional use. Configuration guidelines Follow these guidelines when you configure IP unnumbered on an interface: • An interface cannot borrow an IP address from an unnumbered interface. • Multiple interfaces can use the same unnumbered IP address. • If an interface has multiple IP addresses, only the primary IP address can be borrowed. • The IP address of the borrowing interface varies with that of the borrowed interface. If an IP address is configured for the borrowed interface, the IP address of the borrowing interface is the same as that of the borrowed interface. If no IP address is configured for the borrowed interface, no IP address is assigned for the borrowing interface. Configuration prerequisites Assign a primary IP address to the interface from which you want to borrow the IP address. Alternatively, you may configure the interface to obtain one through BOOTP or DHCP. Configuration procedure To configure IP unnumbered on an interface: Step 1. Enter system view. 2. Enter tunnel interface view. Command system-view interface tunnel number Remarks N/A N/A 23