HP 6125G HP 6125G & 6125G/XG Blade Switches Layer 3 - IP Services Conf - Page 14
Displaying and maintaining ARP
 |
View all HP 6125G manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 14 highlights
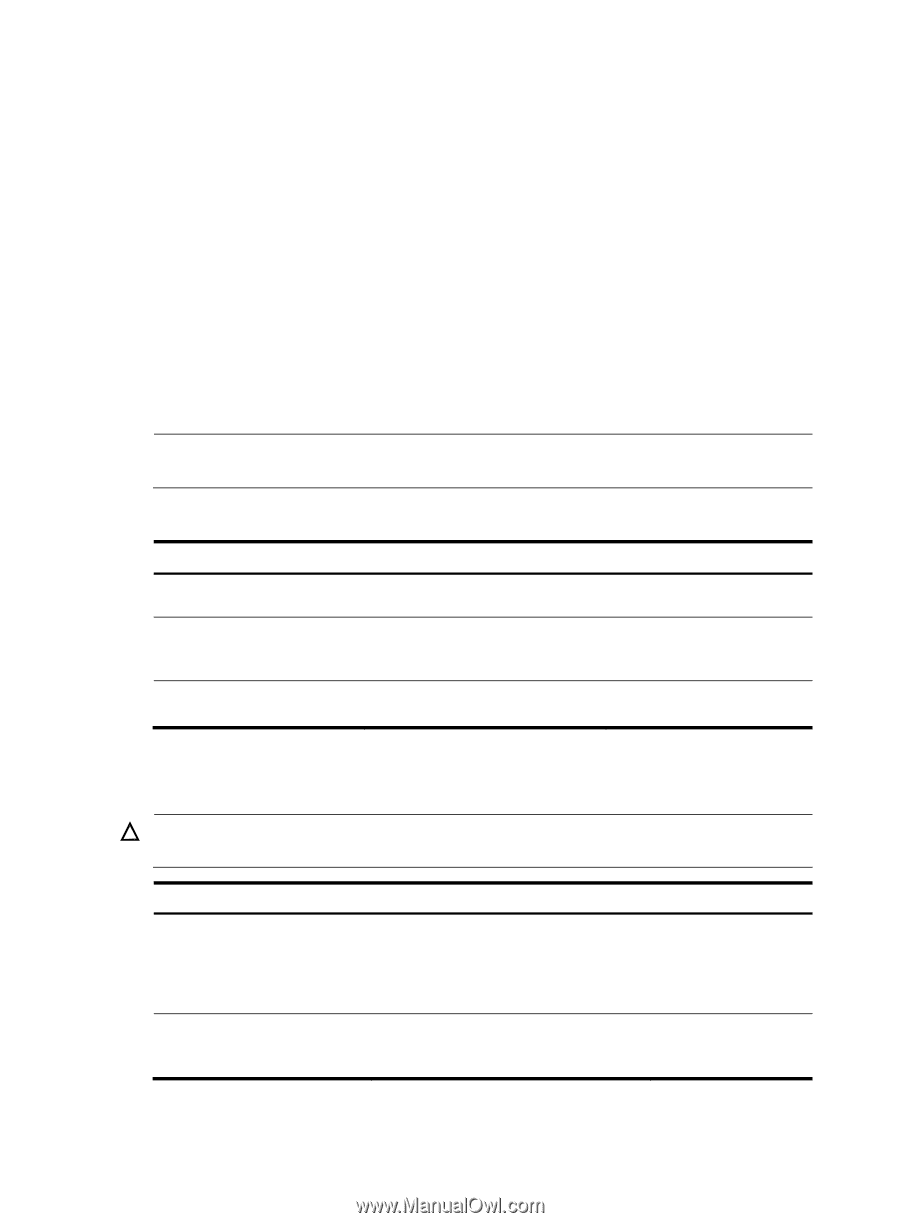
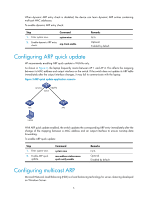
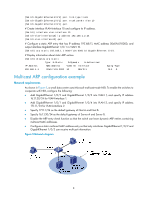
NLB supports load sharing and redundancy among servers within a cluster. To implement fast failover, NLB requires that the switch forwards network traffic to all servers or specified servers in the cluster, and each server filters out unexpected traffic. In a medium or small data center that uses the Windows Server operating system, the proper cooperation of the switch and NLB is very important. For more information about NLB, see the related documents of Windows Sever. Microsoft NLB provides the following packet sending modes to make the switch forward network traffic to all servers or specified servers: • Unicast mode-NLB assigns each cluster member a common MAC address, which is the cluster MAC address, and changes the source MAC address of each sent packet. Thus, the switch cannot add the cluster MAC address to its MAC table. In addition, because the cluster MAC address is unknown to the switch, packets destined to it are forwarded on all the ports of the switch. • Multicast mode-NLB uses a multicast MAC address that is a virtual MAC address for network communication, for example 0300-5e11-1111. • Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP) multicast mode-The switch sends packets only out of the ports that connect to the cluster members rather than all ports. NOTE: Multicast ARP is applicable to only multicast-mode NLB. To configure multicast ARP: Step Command Remarks 1. Disable the ARP entry check function. undo arp check enable N/A arp static ip-address mac-address 2. Configure a static ARP entry. vlan-id interface-type interface-number Optional. [ vpn-instance vpn-instance-name ] 3. Configure a static multicast mac-address multicast mac-address MAC address entry. interface interface-list vlan vlan-id See IP Multicast Command Reference. Displaying and maintaining ARP CAUTION: Clearing ARP entries from the ARP table may cause communication failures. Task Display ARP entries in the ARP table Display the ARP entry for a specified IP address Command display arp [ [ all | dynamic | static ] [ slot slot-number ] | vlan vlan-id | interface interface-type interface-number ] [ count | verbose ] [ | { begin | exclude | include } regular-expression ] display arp ip-address [ slot slot-number ] [ verbose ] [ | { begin | exclude | include } regular-expression ] Remarks Available in any view Available in any view 6