HP 6125G HP 6125G & 6125G/XG Blade Switches Layer 3 - IP Services Conf - Page 129
IPv4 over IPv4 tunneling, Through the embedded IPv4 address
 |
View all HP 6125G manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 129 highlights
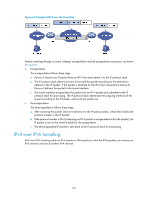
notation. For example, 1.1.1.1 can be represented by 0101:0101. The part that follows 2002:abcd:efgh uniquely identifies a host in a 6to4 network. The tunnel destination is automatically determined by the embedded IPv4 address, which makes it easy to create a 6to4 tunnel. The tunnel can forward IPv6 packets because the 16-bit subnet number of the 64-bit address prefix in 6to4 addresses can be customized and the first 48 bits in the address prefix are fixed to a permanent value and the IPv4 address of the tunnel source or destination. Figure 59 6to4 tunnel 6to4 router 6to4 network Site 1 Device A IPv4 network 6to4 tunnel 6to4 router 6to4 network Site 2 Device B • ISATAP tunneling An ISATAP tunnel is a point-to-multipoint automatic tunnel. The destination of a tunnel can automatically be acquired from the embedded IPv4 address in the destination address of an IPv6 packet. When an ISATAP tunnel is used, the destination address of an IPv6 packet and the IPv6 address of a tunnel interface both adopt special ISATAP addresses. The ISATAP address format is prefix(64bit):0:5EFE:abcd:efgh. The 64-bit prefix is the prefix of a valid IPv6 unicast address, but abcd:efgh is a 32-bit source IPv4 address in hexadecimal, which might not be globally unique. Through the embedded IPv4 address, an ISATAP tunnel can be automatically created to transfer IPv6 packets. The ISATAP tunnel is mainly used for communication between IPv6 routers or between a host and an IPv6 router over an IPv4 network. Figure 60 Principle of ISATAP tunneling IPv4 over IPv4 tunneling IPv4 over IPv4 tunneling (specified in RFC 1853) is developed for IP data packet encapsulation so that data can be transferred from one IPv4 network to another IPv4 network. 121