HP Dc7700 HP Compaq dx7300 and dc7700 Business PC Technical Reference Guide, 1 - Page 178
is ready to receive them. Response and typematic codes are not buffered. If the buffer is full 16
 |
UPC - 882780715318
View all HP Dc7700 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 178 highlights
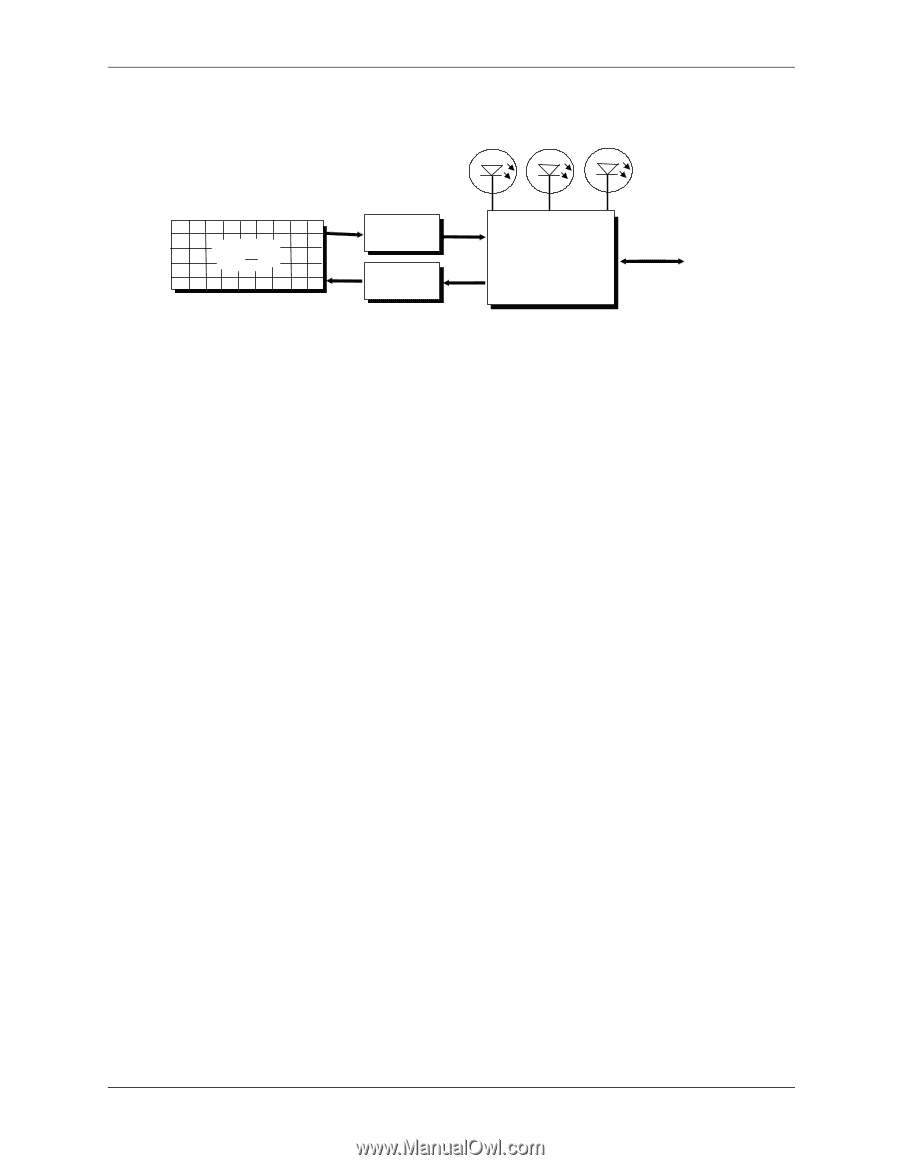
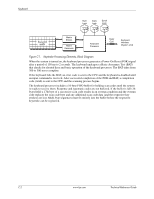
Keyboard Num Lock Caps Lock Scroll Lock Keyswitch Matrix Matrix Drivers Matrix Receivers Keyboard Processor Data/ CLK Keyboard Interface (System Unit) Figure C-1. Keystroke Processing Elements, Block Diagram When the system is turned on, the keyboard processor generates a Power-On Reset (POR) signal after a period of 150 ms to 2 seconds. The keyboard undergoes a Basic Assurance Test (BAT) that checks for shorted keys and basic operation of the keyboard processor. The BAT takes from 300 to 500 ms to complete. If the keyboard fails the BAT, an error code is sent to the CPU and the keyboard is disabled until an input command is received. After successful completion of the POR and BAT, a completion code (AAh) is sent to the CPU and the scanning process begins. The keyboard processor includes a 16-byte FIFO buffer for holding scan codes until the system is ready to receive them. Response and typematic codes are not buffered. If the buffer is full (16 bytes held) a 17th byte of a successive scan code results in an overrun condition and the overrun code replaces the scan code byte and any additional scan code data (and the respective key strokes) are lost. Multi-byte sequences must fit entirely into the buffer before the respective keystroke can be registered. C-2 www.hp.com Technical Reference Guide