Intel 640 User Guide - Page 12
Definition of Terms
 |
UPC - 683728178901
View all Intel 640 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 12 highlights
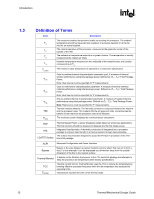
Introduction R 1.3 Definition of Terms Term Description TA TC TE TS TC-MAX ΨCA ΨCS ΨSA TIM PMAX TDP IHS LGA775 Socket The measured ambient temperature locally surrounding the processor. The ambient temperature should be measured just upstream of a passive heatsink or at the fan inlet for an active heatsink. The case temperature of the processor, measured at the geometric center of the topside of the IHS. The ambient air temperature external to a system chassis. This temperature is usually measured at the chassis air inlets. Heatsink temperature measured on the underside of the heatsink base, at a location corresponding to TC. The maximum case temperature as specified in a component specification. Case-to-ambient thermal characterization parameter (psi). A measure of thermal solution performance using total package power. Defined as (TC - TA) / Total Package Power. Note: Heat source must be specified for Ψ measurements. Case-to-sink thermal characterization parameter. A measure of thermal interface material performance using total package power. Defined as (TC - TS) / Total Package Power. Note: Heat source must be specified for Ψ measurements. Sink-to-ambient thermal characterization parameter. A measure of heatsink thermal performance using total package power. Defined as (TS - TA) / Total Package Power. Note: Heat source must be specified for Ψ measurements. Thermal Interface Material: The thermally conductive compound between the heatsink and the processor case. This material fills the air gaps and voids, and enhances the transfer of the heat from the processor case to the heatsink. The maximum power dissipated by a semiconductor component. Thermal Design Power: a power dissipation target based on worst-case applications. Thermal solutions should be designed to dissipate the thermal design power. Integrated Heat Spreader: A thermally conductive lid integrated into a processor package to improve heat transfer to a thermal solution through heat spreading. The surface mount socket designed to accept the Pentium 4 processor in the 775- land LGA package. ACPI Advanced Configuration and Power Interface. Bypass Bypass is the area between a passive heatsink and any object that can act to form a duct. For this example, it can be expressed as a dimension away from the outside dimension of the fins to the nearest surface. Thermal Monitor A feature on the Pentium 4 processor in the 775-land LGA package that attempts to keep the processor die temperature within factory specifications. TCC TDIODE Thermal Control Circuit: Thermal Monitor uses the TCC to reduce die temperature by lowering effective processor frequency when the die temperature has exceeded its operating limits. Temperature reported from the on-die thermal diode. 12 Thermal/Mechanical Design Guide