Intel 640 User Guide - Page 57
Time s, Tdiode C
 |
UPC - 683728178901
View all Intel 640 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 57 highlights
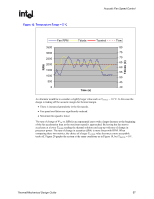
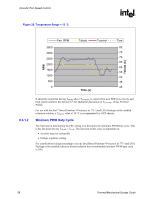
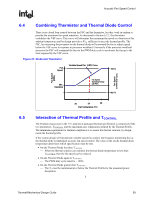
R Figure 19. Temperature Range = 5 °C Acoustic Fan Speed Control RPM Tdiode (C) Fan RPM 3500 3000 2500 2000 1500 1000 500 0 Tdiode Tcontrol Time (s) Tlow 80 75 70 65 60 55 50 45 40 An alternate would be to consider a slightly larger value such as TRANGE = 10 °C. In this case the design is trading off the acoustic margin for thermal margin. • There is increased granularity in the fan speeds. • Fan speed oscillation are significantly reduced • Maximum fan speed is lower The rate of change of ΨCA vs. RPM is an exponential curve with a larger decrease at the beginning of the fan acceleration than as the maximum speed is approached. By having the fan start to accelerate at a lower TDIODE reading the thermal solution can keep up with rate of change in processor power. The rate of change in acoustics (dBA) is more linear with RPM. When comparing these two metrics, the choice of a larger TRANGE value becomes a more acceptable trade off. Figure 20 graphs the system at the same conditions as in Figure 19, but TRANGE = 10°. Thermal/Mechanical Design Guide 57