Intel 640 User Guide - Page 87
Appendix E Board Level PWM and Fan, Speed Control, Requirements
 |
UPC - 683728178901
View all Intel 640 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 87 highlights
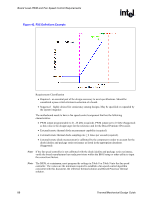
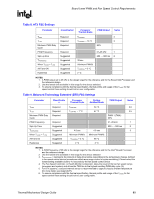
Board Level PWM and Fan Speed Control Requirements R Appendix E Board Level PWM and Fan Speed Control Requirements To use all of the features in the Intel reference heatsink design or the Boxed Intel Pentium 4 Processor in 775-land LGA package, system integrators should verify the following functionality is present in the board design. Refer to the Fan Specification for 4 wire PWM Controlled Fans and Chapter 5 for complete details on the Intel enabled thermal solution. The basics of Fan Speed Control are discussed in Chapter 6; as a review, the FSC definitions are listed in Table 7. Table 7. FSC Definitions Item TDIODE TCONTROL TLOW Hysteresis THIGH All Fans ON Min PWM Spin-up PWM Freq TAVERAGING Definition Temperature reported from the processor on-die thermal diode. TCONTROL is the specification limit for use with the on-die thermal diode The temperature above which the fan will begin to accelerate in response to the on-die thermal diode temperature. The number of degrees below T-control the fans will remain on before slowing down. The temperature at which the fan is operating at full speed (100% PWM Duty Cycle). By specification this is TCONTROL. The processor temperature at which all fans in the system are increased to 100% Duty Cycle. Minimum pulse width modulation (% duty cycle) that the fans will run at when TDIODE is less than TLOW. Amount of time fan is run at 100% duty cycle to overcome fan inertia. The operating frequency of the PWM signal. The time (in seconds) that elapses while the fan is gradually sped up in response to a processor temperature spike. Thermal/Mechanical Design Guide 87