D-Link DSN-540 Software User's Guide for DSN-1100-10 - Page 124
Working with VLANs
 |
UPC - 790069324017
View all D-Link DSN-540 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 124 highlights
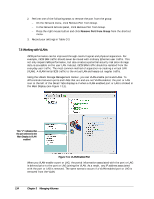
2. Perform one of the following steps to remove the port from the group: - On the Network menu, click Remove Port from Group. - In the Network Actions panel, click Remove Port from Group. - Press the right mouse button and click Remove Port from Group from the shortcut menu. 3. Record your settings in Table C-3. 7.6 Working with VLANs iSCSI performance can be improved through careful logical and physical separation. For example, iSCSI SAN traffic should never be mixed with ordinary Ethernet user traffic. This not only impairs SAN performance, but also creates a potential security risk since storage data is accessible on the user LAN. Instead, iSCSI SAN traffic should be isolated from the everyday user traffic. The most common method of separation is creating a virtual LAN (VLAN). A VLAN limits iSCSI traffic to the virtual LAN and keeps out regular traffic. Using the xStack Storage Management Center, you can VLAN-enable ports and LAGs. To differentiate between ports and LAGs that are and are not VLAN-enabled, the port or LAG icon to the left of the Detail Tabs displays a V when a VLAN-enabled port or LAG is clicked in the Main Display (see Figure 7-11). This "V" indicates that the port selected in the Main Display is VLAN enabled Figure 7-11. VLAN-Enabled Port When you VLAN-enable a port or LAG, the portal information associated with the port or LAG is deleted prior to the port or LAG joining the VLAN. As a result, any IP address associated with the port or LAG is removed. The same scenario occurs if a VLAN-enabled port or LAG is removed from the VLAN. 114 Chapter 3 Managing Volumes