Epson FX-185 User Manual - Page 220
Attribute byte, Proportional print, Pins chosen by attribute byte
 |
View all Epson FX-185 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 220 highlights
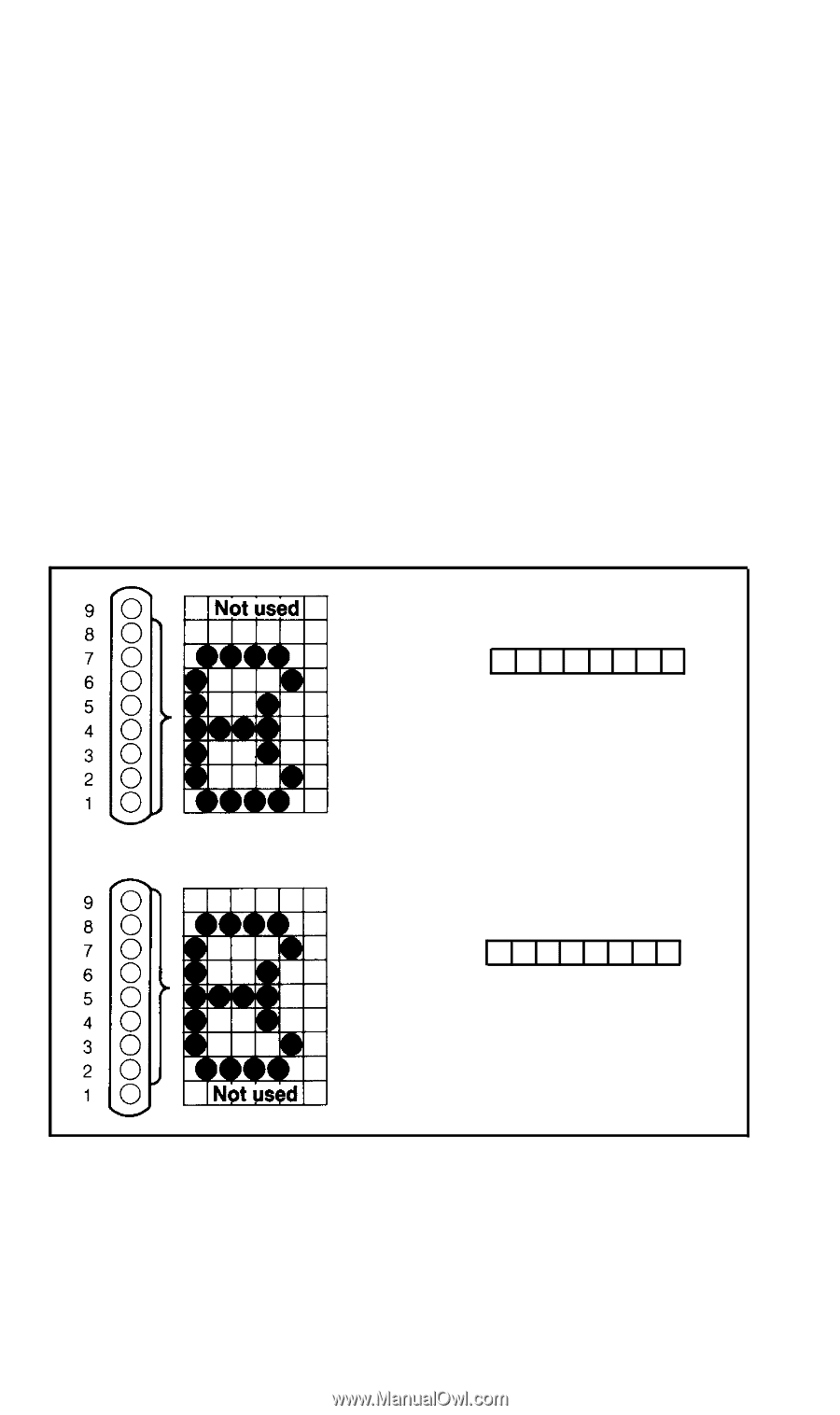
Attribute byte The attribute byte is the first of the 12 data numbers required to define any character. At print time it controls two aspects of the way the character is printed. First, it determines which 8 pins of the print head are used to print the character. For most characters, the top 8 pins are used, but for lowercase characters with descenders (like g and p), the bottom 8 pins can be used. So how does the attribute byte determine which 8 pins are used? At print time, the printer checks the attribute byte before each character is printed. If the high-order bit is on, the top 8 pins of the print head are used; if the high-order bit is off, the bottom 8 are used. To put it another way, if the attribute byte for a given character is 128 or greater, the top 8 pins are used; if it is 127 or less, the bottom 8 are used. Figure 15-4 demonstrates these choices. ATTRIBUTE BYTE OFF 0 128 64 32 16 8 4 2 1 If attribute byte is less than 128, bottom eight pins are used ATTRIBUTE BYTE ON 1 128 64 32 16 8 4 2 1 If attribute byte is 128 or greater, top eight pins are used Figure 15-4. Pins chosen by attribute byte Proportional print The attribute byte also contains information used to print a character in Proportional Mode. It tells the printer in which columns to start and stop printing for each character. If you label the 11 columns deter- 203