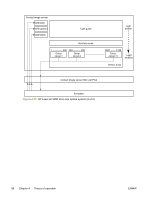
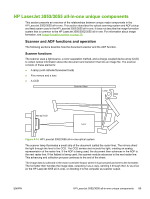
HP LaserJet 3052 Service Manual - Page 112
Fax functions and operation (HP LaserJet 3050 all-in-one and HP LaserJet 3055 all-in-one only)
 |
View all HP LaserJet 3052 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 112 highlights
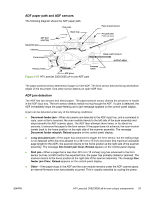
Fax functions and operation (HP LaserJet 3050 all-in-one and HP LaserJet 3055 all-in-one only) The following sections describe the all-in-one fax capabilities. Computer and network security features The HP LaserJet 3050/3055 all-in-one can send and receive fax data over telephone lines that conform to public switch telephone network (PSTN) standards. The secure fax protocols make it impossible for computer viruses to be transferred from the telephone line to a computer or network. The following all-in-one features prevent virus transmission: ● No direct connection exists between the fax line and any devices that are connected to the USB or Ethernet ports. ● The internal firmware cannot be modified through the fax connection. ● All fax communications go through the fax subsystem, which does not use Internet data-exchange protocols. PSTN operation The public switched telephone network (PSTN) operates through a central office (CO) that generates a constant voltage on the TIP and RING wires (48 V, usually). A device goes on-hook by connecting impedance (such as 600 ohms for the U.S.) across the TIP and RING so that a line current can flow. The CO can detect this current and can send impulses like dial tones. The all-in-one generates more signaling tones, such as dialing digits, to tell the CO how to connect the call. The all-in-one can also detect tones, such as a busy tone from the CO, that tell it how to behave. When the call is finally connected, the CO behaves like a piece of wire connecting the sender and receiver. This is the period during which all of the fax signaling and data transfer occurs. When a call is completed, the circuit opens again and the line-current flow ceases, removing the CO connection from both the sender and the receiver. On most phone systems, the TIP and RING wires appear on pins 3 and 4 of the RJ-11 modular jack (the one on the LIU). These two wires do not have to be polarized because all the equipment works with either TIP or RING on pin 3 and the other wire on pin 4. This means that cables of either polarity can interconnect and will still work. These basic functions of PSTN operation are assumed in the design of the fax subsystem. The all-inone generates and detects the signaling tones, currents, and data signals that are required to transmit and receive faxes on the PSTN. 92 Chapter 4 Theory of operation ENWW