Netgear GS752TP GS728TP/GS728TPP/GS752TP Software Administration Manual - Page 133
Con ARP, The Address Resolution Protocol ARP associates a Layer 2 MAC address with a Layer 3
 |
View all Netgear GS752TP manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 133 highlights
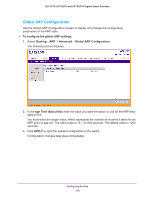
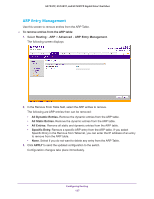
GS752TP, GS728TP, and GS728TPP Gigabit Smart Switches Configure ARP The Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) associates a Layer 2 MAC address with a Layer 3 IPv4 address. The switch software features both dynamic and manual ARP configuration. With manual ARP configuration, you can statically add entries to the ARP table. ARP is a necessary part of the Internet Protocol (IP) and is used to translate an IP address to a media (MAC) address, defined by a local area network (LAN) such as Ethernet. A station needing to send an IP packet must learn the MAC address of the IP destination, or of the next hop router, if the destination is not on the same subnet. Learning is achieved by broadcasting an ARP request packet, to which the intended recipient responds with a unicast ARP reply containing its MAC address. Once learned, the MAC address is used in the destination address field of the Layer 2 header prepended to the IP packet. The ARP cache is a table maintained locally in each station on a network. ARP cache entries are learned by examining the source information in the ARP packet payload fields, regardless of whether it is an ARP request or response. Thus, when an ARP request is broadcast to all stations on a LAN segment or virtual LAN (VLAN), every recipient has the opportunity to store the sender's IP and MAC address in its respective ARP cache. The ARP response, being unicast, is normally seen only by the requestor, who stores the sender information in its ARP cache. Newer information always replaces existing content in the ARP cache. The NETGEAR switches support 1024 ARP entries in switch mode and approximately 100 in router mode. These entries include dynamic and static ARP entries. Devices can be moved in a network, which means the IP address that was at one time associated with a certain MAC address is now found using a different MAC address, or might have disappeared from the network altogether (that is, it has been reconfigured, disconnected, or powered off). This leads to stale information in the ARP cache unless entries are updated in reaction to new information seen on the network, periodically refreshed to determine if an address still exists, or removed from the cache if the entry has not been identified as a sender of an ARP packet during an ageout interval, specified through configuration. From the ARP menu, you can access features described in the following sections: • ARP Cache • ARP Entry Configuration • Global ARP Configuration • ARP Entry Management Configuring Routing 133