Netgear GS752TP GS728TP/GS728TPP/GS752TP Software Administration Manual - Page 150
IPv6 Class Configuration, Source L4 Port, Destination IP, IP DSCP, Precedence Value, APPLY
 |
View all Netgear GS752TP manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 150 highlights
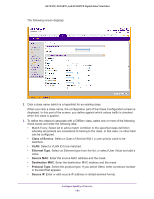
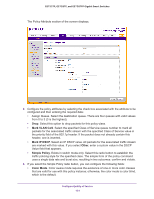
GS752TP, GS728TP, and GS728TPP Gigabit Smart Switches • Source L4 Port. Select the desired L4 keyword from the list on which the rule can be based. The options are Other, domain, echo, ftp, ftpdata, http, smtp, snmp, telnet, tftp, or www. If you select Other, enter a user-defined port ID. • Destination IP. Enter a valid destination IP address in dotted-decimal format. • Destination L4 Port. Enter the desired L4 keyword from the list on which the rule can be based. The options are Other, domain, echo, ftp, ftpdata, http, smtp, snmp, telnet, tftp, or www. If you select Other, the screen refreshes and a port ID field appears. • Service Type: • IP DSCP. Select the DSCP type from the list or enter a DSCP value to match. If you select Other, enter a custom value in the DSCP Value field that appears. The range is 0-63. • Precedence Value. Enter a precedence value. 4. Click APPLY to send the updated configuration to the switch. Configuration changes occur immediately. IPv6 Class Configuration The IPv6 Class Configuration feature extends the existing QoS ACL and DiffServ functionality by providing support for IPv6 packet classification. An Ethernet IPv6 packet is distinguished from an IPv4 packet by its unique EtherType value, so all IPv6 classifiers include the EtherType field. An IPv6 access list serves the same purpose as its IPv4 counterpart. When you define a class, you must specify if this class rule is for IPv4 or for IPv6 packets by using the correct screen (either Class Configuration or IPv6 Class Configuration). The destination and source IPv6 addresses use a prefix length value instead of an individual mask to qualify it as a subnet address or a host address. The flow label is a 20-bit number that is unique to an IPv6 packet, used by end stations to signify some form of Quality of Service (QoS) handling in routers. Packets that match an IPv6 classifier are allowed only to be marked using the 802.1p (CoS) field or the IP DSCP field in the traffic class octet. IP precedence is not defined for IPv6: this is not an appropriate type of packet marking. IPv6 ACL and DiffServ assignment are appropriate for LAG interfaces. The procedures described by an ACL or DiffServ policy are equally applicable on a port or LAG interface. To configure an IPv6 class: 1. Select QoS DiffServ Advanced IPv6 Class Configuration. Configure Quality of Service 150