Cisco 521SG Administration Guide - Page 125
Configuring the Protocol on a Cisco SPA525G or Cisco SPA525G2
 |
UPC - 882658248993
View all Cisco 521SG manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 125 highlights
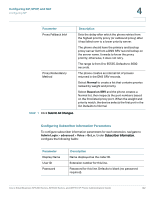
Configuring SIP, SPCP, and NAT Managing NAT Transversal with Cisco IP Phones 4 Configuring the Protocol on a Cisco SPA525G or Cisco SPA525G2 To configure the protocol on the Cisco SPA525G or Cisco SPA525G2, navigate to Admin Login > advanced > Voice > System. Under System Configuration in the SPA525-protocol field, choose SCCP or SIP. To configure the phone to automatically detect the protocol being used on the network that it is connected to, in the SPA525-auto-detect-sccp field, choose yes. Configuring the Protocol on a Cisco SPA300 Series or Cisco SPA500 Series IP Phone To configure the protocol on a Cisco SPA300 Series or Cisco SPA500 Series IP phone, navigate to Admin Login > advanced > Voice > System. Under System Configuration in the Signaling Protocol field, choose SCCP or SIP. To configure the phone to automatically detect the protocol being used on the network that it is connected to, in the SPCP Auto-detect field, choose yes. The phone defaults to SIP unless it detects a Cisco Unified Communications device. When set to no, the phone uses the protocol set in the Signaling Protocol field. The Cisco SPA301 or the Cisco SPA501G can be configured by using the IVR. See Using IVR on IP Phones Without Screens for more information. Managing NAT Transversal with Cisco IP Phones Network Address Translation (NAT) allows multiple devices to share a single, public, routable, IP address to establish connections over the Internet. NAT is present in many broadband access devices to translate public and private IP addresses. For VoIP to co-exist with NAT, NAT traversal is required. Not all service providers provide NAT traversal. If your service provider does not provide NAT traversal, you have several options: • NAT Mapping with Session Border Controller • NAT Mapping with SIP-ALG Router • NAT Mapping with a Static IP Address • NAT Mapping with STUN Cisco Small Business SPA300 Series, SPA500 Series, and WIP310 IP Phone Administration Guide 124