Cisco 7921G Administration Guide - Page 35
Components of the VoIP Wireless Network
 |
UPC - 882658123108
View all Cisco 7921G manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 35 highlights
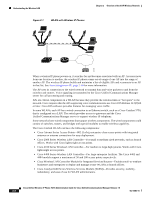
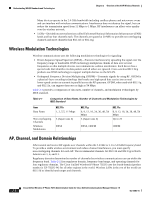
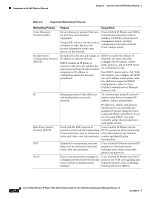
Chapter 2 Overview of the VoIP Wireless Network Components of the VoIP Wireless Network CCKM, a centralized key management protocol, provides a cache of session credentials on the wireless domain server (WDS). As the phone roams from one AP to the next, CCKM compresses the number of message exchanges during roaming by providing a master key stored on the WDS for the AP to use. The reassociation exchange is reduced to two messages, thereby reducing the roaming time. For details about CCKM, refer to the "Cisco Fast Secure Roaming Application Note" at: http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/hw/wireless/ps4570/prod_technical_reference09186a00801 c5223.html Note In dual band WLANs, it is possible to roam between 2.4 GHz bands (802.11b/g) and 5 GHz bands (802.11a). The phone moves out of range of one AP using one band and into the range of another that has the same SSID but is using a different band. This can cause gaps in voice communications. To avoid these communication gaps, try to use only one band for voice communications. Related Topics • Voice QoS in a Wireless Network, page 2-10 • Interacting with Cisco Unified Wireless APs, page 2-9 • VoIP WLAN Configuration, page 2-18 Components of the VoIP Wireless Network The wireless IP phone must interact with several network components in the WLAN to successfully place and receive calls. The following topics describe network components: • Networking Protocols Used with Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phones, page 2-7 • Interacting with Cisco Unified Wireless APs, page 2-9 • Voice QoS in a Wireless Network, page 2-10 • Interacting with Cisco Unified Communications Manager, page 2-12 • Interacting with the DHCP Server, page 2-13 Networking Protocols Used with Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phones Cisco Unified IP Phones support several networking protocols for voice communication. Table 2-3 describes the networking protocols that the Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7921G supports. OL-15985-01 Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7921G Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager Release 7.0 2-7