Cisco 7912G Administration Guide - Page 32
Networking Protocol, Purpose, Usage Notes, Modifying DHCP Settings, Configuring IP Settings - manual
 |
UPC - 746320852409
View all Cisco 7912G manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 32 highlights
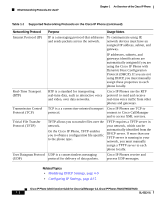
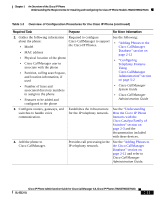
What Networking Protocols Are Used? Chapter 1 An Overview of the Cisco IP Phone Table 1-1 Supported Networking Protocols on the Cisco IP Phone (continued) Networking Protocol Purpose Usage Notes Internet Protocol (IP) IP is a messaging protocol that addresses and sends packets across the network. To communicate using IP, network devices must have an assigned IP address, subnet, and gateway. IP addresses, subnets, and gateways identifications are automatically assigned if you are using the Cisco IP Phone with Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP). If you are not using DHCP, you must manually assign these properties to each phone locally. Real-Time Transport (RTP) RTP is a standard for transporting real-time data, such as interactive voice and video, over data networks. Cisco IP Phones use the RTP protocol to send and receive real-time voice traffic from other phones and gateways. Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) TCP is a a connection-oriented transport Cisco IP Phones use TCP to protocol. connect to Cisco CallManager and to access XML services. Trivial File Transfer Protocol (TFTP) TFTP allows you to transfer files over the network. On the Cisco IP Phone, TFTP enables you to obtain a configuration file specific to the phone type. TFTP requires a TFTP server in your network, which can be automatically identified from the DHCP server. If more than one TFTP server is running in your network, you must manually assign a TFTP server to each phone locally. User Datagram Protocol UDP is a connectionless messaging (UDP) protocol for delivery of data packets. Cisco IP Phones receive and process UDP messages. Related Topics • Modifying DHCP Settings, page 4-9 • Configuring IP Settings, page 4-15 Cisco IP Phone Administration Guide for Cisco CallManager 3.3, Cisco IP Phones 7902G/7905G/7912G 1-8 OL-6313-01