Dell PowerVault NX3610 User Manual - Page 63
Configuring DNS, Viewing DNS Servers, Adding DNS Servers And DNS Suffixes, Managing Static Routes
 |
View all Dell PowerVault NX3610 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 63 highlights
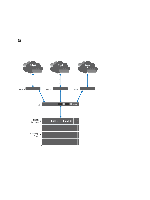
The solution is to define, in addition to a default gateway, a specific gateway for certain subnets-configuring static routes. To do this you must describe each subnet in your network and identify the most suitable gateway to access that subnet. You do not have to do so for the entire network - a default gateway is most suitable when performance is not an issue. You can select when and where to use static routes to best meet your performance needs. Configuring DNS Domain Name System (DNS) is the name resolution service that enables users to locate computers on a network or on the Internet (TCP/IP network) by using the domain name. The DNS server maintains a database of domain names (host names) and their corresponding IP addresses providing name-to-address and address-to-name resolution services on the IP network. You can configure one or more external DNS server (external to NAS cluster solution but within the site) to be used for name resolutions. Viewing DNS Servers To view a list of existing DNS servers and their parameters, select Cluster Management → Network → DNS Configuration, the DNS Configuration page displays the list of existing DNS servers and their parameters. Adding DNS Servers And DNS Suffixes 1. Select Cluster Management → Network → DNS Configuration. The DNS Configuration page is displayed. 2. To add a DNS server, click Add DNS Server. A new empty row is added to the list of DNS servers. 3. Set the IP address of the client environment primary DNS. 4. To add a DNS suffix, click Add DNS Suffix. A new empty row is added to the list of DNS suffixes. 5. Enter the DNS suffixes in order of precedence. 6. Click Save Changes. Removing DNS Servers And DNS Suffixes 1. Select Cluster Management → Network → DNS Configuration. The DNS Configuration page displays the list of existing DNS servers and their parameters. 2. Select the appropriate DNS server and/or DNS suffix and click Delete. A message prompts you that the deleted DNS server saves all other changes that have been made. 3. Click OK. Managing Static Routes To minimize hops between routers, static routes are suggested in routed networks when there are multiple direct paths from the NAS cluster solution to various routers. 63