Epson LQ 1050 Technical Manual - Page 192
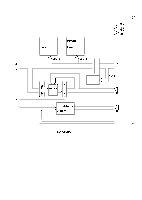
A-3. OP Code Fetch Timing
 |
View all Epson LQ 1050 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 192 highlights
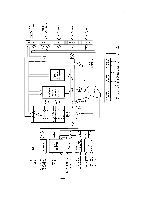
REV.-A q CPU Timing "['''"" Refer to Figures A-3 through A-5 for CPU timing diagrams. Three oscillations define one state. The OP code fetch requires four states; during TI to T3, program memory is read; instructions are interpreted during T4. Address bus lines 15-8 are output from T1 to T4. Address but lines 7-O (PD7-0) are used in the multiplex mode; the address is latched during T1 at the ALE signal. Since the memory addressed is enabled after disengaging the driver (AD7-0), ~ is output from T1 -T3, fetched at T3, and processed internally at T4. The ALE and RD signals are executed from T1-T3; the OP code fetch for these two signals is performed at T4. The WR signal is output from the middle of T 1 to the beginning of T3. The address and ALE timing is the same as that for memory read; however following address output AD7-O (PD7-0) are not disabled, and write data is output at AD7-O at the beginning of T1 and the end of T3. NOTE: When PD7-O are set to the multiplexed address/data-bus (AD7-0) to the address bus (AB7-0), the ~ and WR signals in the machine cycle are HIGH when memory is not being accessed. CLOCK ALE AB15 -8 (PF7 -O) AD7 -o (PD7 -O) Y ADDRESS x A D D R E S S }- - - - < OP CODE / x >---c Figure A-3. OP Code Fetch Timing T1 T2 T3 CLOCK ~ AB15 -8 (PF7 -0) AD7 -o (PD7 -O) x ADDRESS x x A D D R E S S }- --< READ DATA >--- c Figure A-4. Memory Read Timing CLOCK AB15 -8 (PF7 -0) AD7 -0 (PD7 -0) x ADDRESS x x x ADDRESS WRITE DATA Figure A-5. Memory Write Timing A-6