Epson LQ 1050 Technical Manual - Page 81
DIP Switch Circuit
 |
View all Epson LQ 1050 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 81 highlights
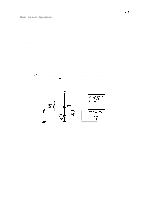
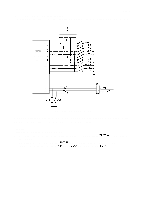
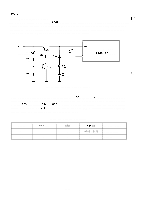
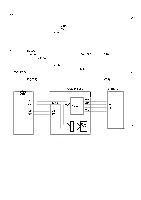
REV.-A 2.3.4.3 DIP Switch Circuit and Jumpers The printer has two types of DIP switches and two jumpers. Figure 2-31 shows the DIP switch circuit. PBO 1 CPU : (781OHG) 4 (46) : 7 AN3 4 +5V 1 I RM 1 1 R65 IK PA? Vbv"r PA6 M R1OO IK J1 SW2-4 CN 1 36 m - 14 AUTO FEtD XT k Figure 2-31. DIP Switch Circuit DIP switch settings are read by the DIP switch circuit whenever the printer power is turned on and whenever the INIT signal is sent to the printer from the host computer. Jumpers There are two jumpers on the PEGX board. J 1: Determines whether or not the internally fixed printer selection signal (SLCTIN) is selected by the host computer. When jumper J 1 is connected, the SLCTIN signal is internally fixed (always selected). J2: Switches the memory capacity (5 12K bits or 256K bits) for the PROM (IC4A). 2-37