Epson LQ 1050 Technical Manual - Page 79
Data Transmission Timing
 |
View all Epson LQ 1050 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 79 highlights
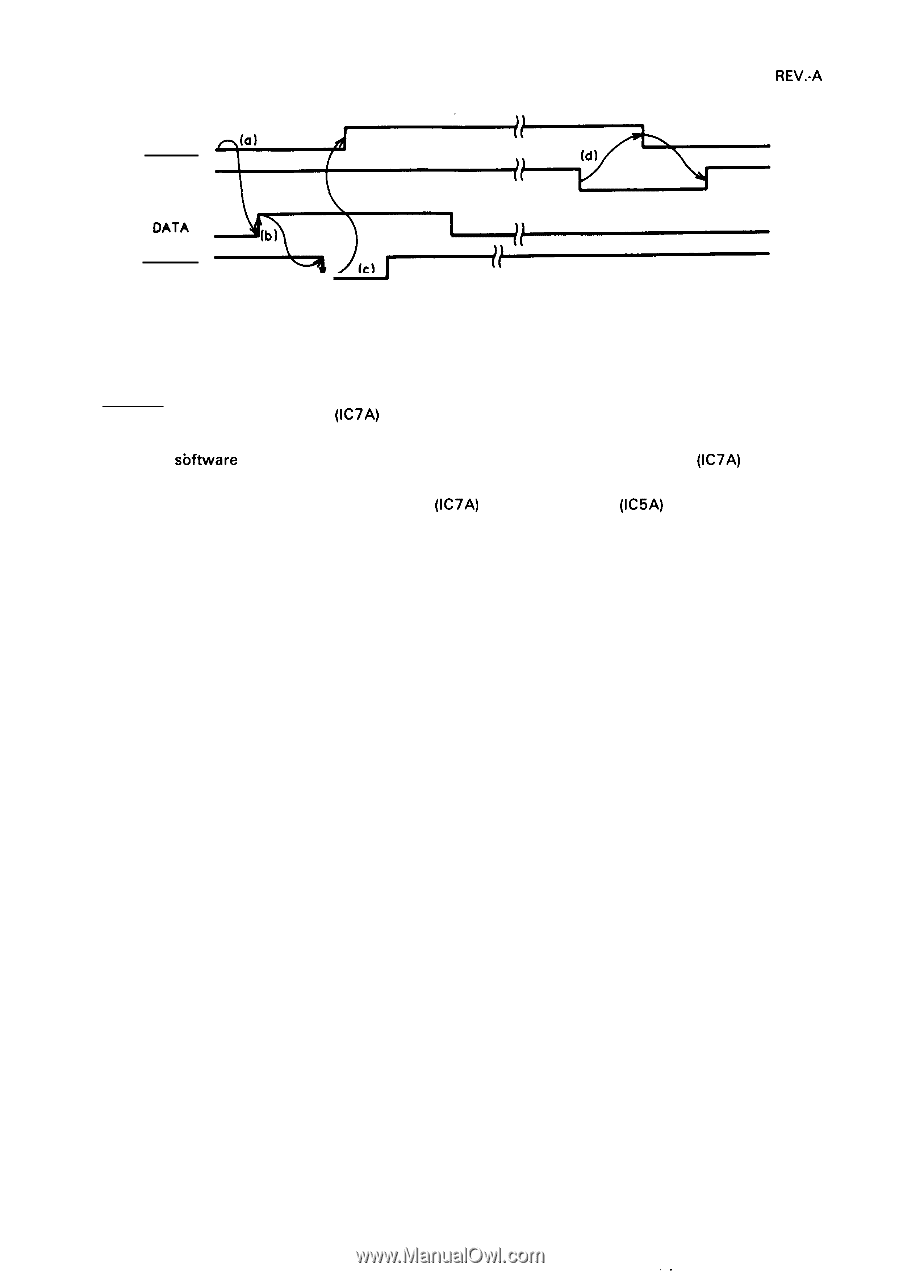
REV.-A BUSY ACKNLG DATA STROBE v .-. 4 Figure 2-29. Data Transmission Timing Sequence 1. Data transmitted from the host computer is latched into the gate array at the trailing edge of the STROBE signal. The gate array (IC7A) then outputs the BUSY signal to the host computer. 2. The CPU reads the data latched in the gate array and clears the BUSY signal. However, the CPU also outputs a sbftware generated BUSY signal to the host computer via the gate array (IC7A) so that the BUSY signal to the host computer remains HIGH. 3. The CPU stores the data from the gate array (IC7A) in the input buffer (IC5A) and informs the gate array of completion of data processing through the data bus. The gate array outputs the ACK signal to the host computer to indicate that 1 byte of data has been processed. The CPU then clears the BUSY signal. 4. The printer is now ready to accept the next data byte. 2-35 ,,