Epson LQ 1050 Technical Manual - Page 92
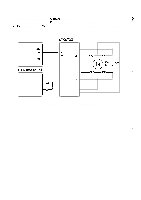
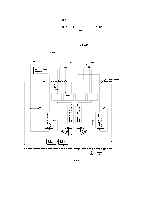
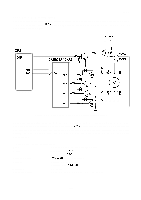
Carriage Motor Control Circuit
 |
View all Epson LQ 1050 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 92 highlights
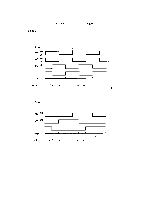
REV.-A Detailed Operation (Figure 2-39.) g,:, * q When the + 5V supply voltage is applied to the STK6722HZ (IC2A), the triangular waveform circuit "'" in the H-IC starts oscillation and outputs the reference signal (approx. 24KHz) for chopper control. q Because the output of comparator IC2 (point Q) is high (input at the plus side > input at the minus side) when the printer power is turned on, TR7 turns on and base current flows to TR 1. When a high signal (AO 1: low) is input to the base of TR3, TR3 turns on, and coil current ICA flows from VCCI to TR 1 to phase A to D5 to TR3 to R 13. ICA gradually increases due to the reactance of the motor coil. Voltage VR13 across limiter resistance R13 increases. When VR13 becomes the same as the VREF at pin 8 (from the reference voltage generation circuit), the output of IC2 (point Q) goes low, TR7 turns off, and TR 1 turns off. Then ICA starts decreasing. When VR13 becomes less than VREF, the output of IC2 goes high again. q The surge voltage (also called flyback voltage) generated when TR3 is cut off by the zener diode ZD 1 (approx. 47V) between the collector and base of transistor Q5, and is absorbed by transistor Q5 to protect TR3 from being damaged. q When the carriage motor stops, the motor drive pulses are fixed at a set value to hold the carriage motor. At this time, H-IC is powered down to prevent it from overheating. When the power down ; operation is performed (when the carriage motor is held), PD 1 of the E05A 16GA (IC7A) goes low, '"--- and TR 11 turns on to drop the reference voltage at the plus side of IC2. As a result, the load on VCOMAB is reduced and H-IC is effectively powered down, At this time, approximately 5V is supplied to VCOMAB by PWM control. cot -8 '"'I 'w+ I I 1 1W " ld'A T1 I II 1 Ott I 1 I I .W . -,,. K '7:F T 1 II t II - I 1 1 I I ,I I I 1 1T Figure 2-39. Carriage Motor Control Circuit 2-48