HP P2000 HP P2000 G3 MSA System SMU Reference Guide - Page 143
Using SMI-S, SMI-S overview, Key components, WBEM, CIM, SLP, Profiles
 |
View all HP P2000 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 143 highlights
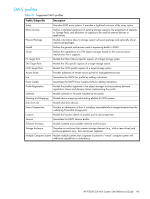
C Using SMI-S This appendix provides information for network administrators who are managing the P2000 G3 MSA System from a storage management application through the Storage Management Initiative Specification (SMI-S). SMI-S is a Storage Networking Industry Association (SNIA) standard that enables interoperable management for storage networks and storage devices. SMI-S overview SMI-S replaces multiple disparate managed object models, protocols, and transports with a single object-oriented model for each type of component in a storage network. The specification was created by SNIA to standardize storage management solutions. SMI-S enables management applications to support storage devices from multiple vendors quickly and reliably because they are no longer proprietary. SMI-S detects and manages storage elements by type, not by vendor. Key components The key SMI-S components are: • Web-based Enterprise Management (WBEM) • Common Information Model (CIM) • Service Location Protocol (SLP) WBEM WBEM is a set of management and internet standard technologies developed to unify the management of enterprise computing environments. WBEM includes the following specifications: • xmlCIM: defines XML elements, conforming to Document Type Definition (DTD), which can be used to represent CIM classes and instances • CIM Operations over HTTP: defines a mapping of CIM operations onto HTTP; used as a transport mechanism CIM CIM, the data model for WBEM, provides a common definition of management information for systems, networks, applications and services, and allows for vendor extensions. SMI-S is the interpretation of CIM for storage. It provides a consistent definition and structure of data, using object-oriented techniques. The standard language used to define elements of CIM is Managed Object Format (MOF). Unified Modeling Language (UML) is used to create a graphical representation (using boxes and lines) of objects and relationships. SLP SLP enables computers and other devices to find services in a local area network without prior configuration. SLP has been designed to scale from small, unmanaged networks to large enterprise networks Profiles SMI-S is organized around profiles, which describe objects relevant for a class of storage subsystem. SMI-S includes profiles for arrays, Fibre Channel host bus adapters (HBAs), Fibre Channel switches, and tape libraries. Other storage devices are expected to be added in the future. Profiles are registered with the CIM server and advertised to clients using SLP. HP SIM determines which profiles it intends to manage, and then uses the CIM model to discover the actual configurations and capabilities. HP P2000 G3 MSA System SMU Reference Guide 143