HP AirLife 100 Compaq AirLife 100 - User Guide - Page 104
Data connection types, HSPA, UMTS, 3G & WCDMA, GPRS/EDGE
 |
View all HP AirLife 100 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 104 highlights
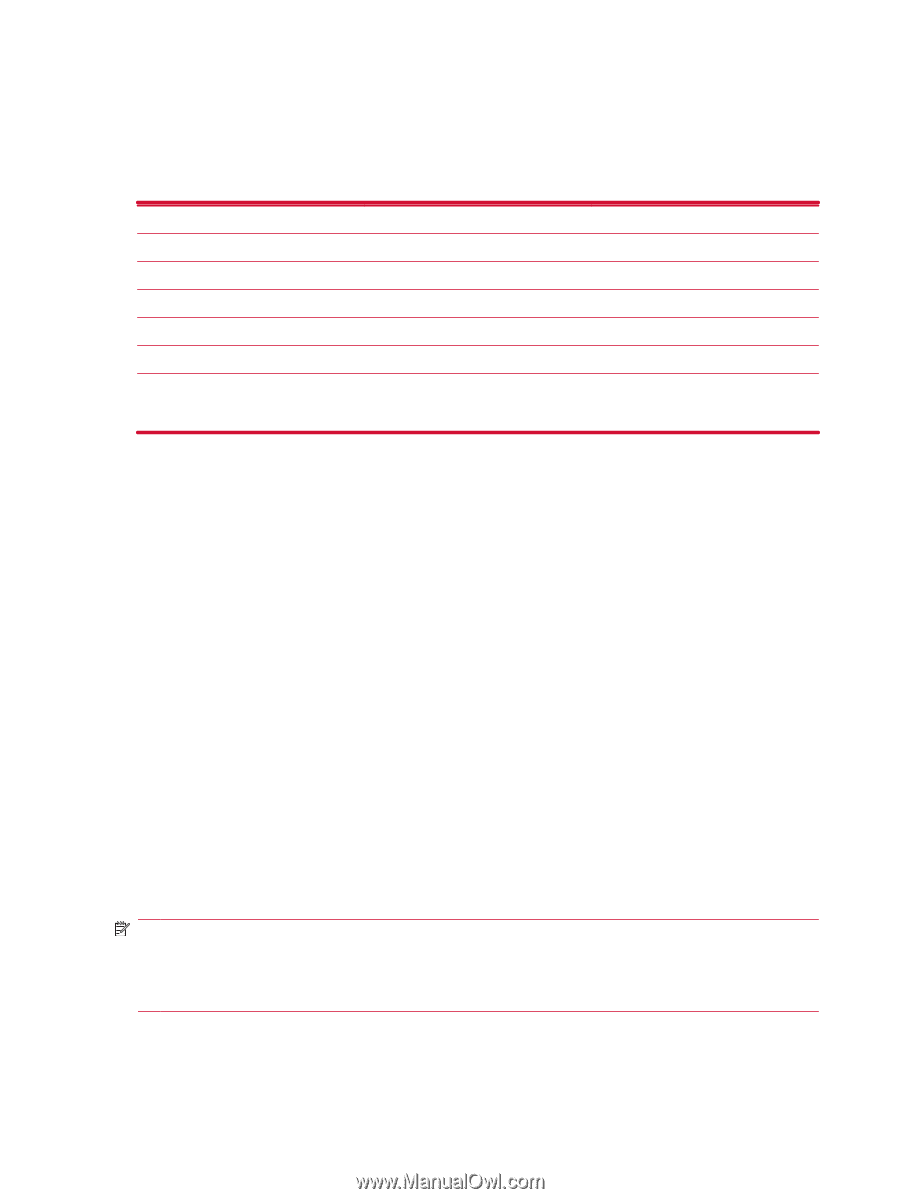
Data connection types Your AirLife supports different types of 2G and 3G connection standards over cellular networks as well as Wi-Fi. The table below provides brief information about the connection standards supported by your AirLife and the features each standard provides: Connection Standard HSPA UMTS EDGE GPRS GSM Wi-Fi Technology Generation 3.5G 3G 2.75G 2.5G 2G 802.11b/g (Supports channels 1-13) Supports Data Yes Yes Yes Yes No Yes HSPA High Speed Packet Access (HSPA), also known as 3.5G, is an enhancement of UMTS which is based on 3G technology, and offers faster data speeds. Your AirLife supports HSPA from 3.6 to 7.2 Mbps for high speed downloads and 2 Mbps for high speed uploads. AirLife also supports HSPA over four different frequency bands (850/900/1900/2100). When HSPA is available, AirLife uses that technology and reverts back to UMTS or GSM/GPRS/EDGE if HSPA is unavailable. UMTS, 3G & WCDMA Universal Mobile Telecommunications System (UMTS) is one of the third-generation (3G) mobile telecommunications technologies, which is also being developed into a 4G technology. The most common form of UMTS uses WCDMA. UMTS is a complete network system, it covers the radio access network (UMTS Terrestrial Radio Access Network, or UTRAN), the core network (Mobile Application Part, or MAP), as well as authentication of users via USIM cards (Subscriber Identity Module). Unlike EDGE, UMTS requires new base stations and new frequency allocations, but it is closely related to GSM/EDGE because it borrows and builds upon concepts from GSM. Most UMTS devices support GSM. The name UMTS is usually used in Europe. Outside of Europe, the system is also known by other names, but is often just referred to as 3G. GPRS/EDGE The GPRS/EDGE technology enables the cellular network to be used for messaging, to access a corporate network, or the Internet. NOTE: EDGE is an enhancement to GPRS technology and enables higher speed data connections than GPRS. This means faster phone multimedia capabilities such as sending and receiving SMS/ MMS messages, and sharing video clips. Check with your service provider to see if they support EDGE technology. If your service provider does not support the EDGE network, the AirLife defaults to GPRS. 96 Chapter 17 Data connection