HP P4000 9.0 HP StorageWorks P4000 SAN Solution User Guide - Page 58
Mixing RAID configurations, more disk space than RAID 5. - calculator
 |
View all HP P4000 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 58 highlights
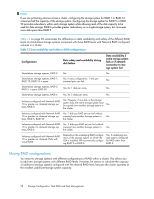
NOTE: If you are protecting volumes across a cluster, configuring the storage system for RAID 1 or RAID 10 consumes half the capacity of the storage system. Configuring the storage system for RAID 5 or RAID 50 provides redundancy within each storage system while allowing most of the disk capacity to be used for data storage. RAID 6 provides greater redundancy on a single storage system, but consumes more disk space than RAID 5. Table 12 on page 58 summarizes the differences in data availability and safety of the different RAID levels on stand-alone storage systems compared with those RAID levels with Network RAID configured volumes in a cluster. Table 12 Data availability and safety in RAID configurations Configuration Data safety and availability during disk failure Data availability if entire storage system fails or if network connection to storage system lost Stand-alone storage systems, RAID 0 No No Stand-alone storage systems, RAID 1, RAID 10, RAID 10 + spare Yes. In any configuration, 1 disk per mirrored pair can fail. No Stand-alone storage systems, RAID 5, RAID 5 + spare, RAID 50 Yes, for 1 disk per array No Stand-alone storage systems, RAID 6 Yes, for 2 disks per array No Volumes configured with Network RAID10 or greater on clustered storage systems, RAID 0 Yes. However, if any disk in the storage system fails, the entire storage system must be copied from another storage system in the cluster. Yes Volumes configured with Network RAID- Yes. 1 disk per RAID set can fail without 10 or greater on clustered storage sys- copying from another storage system in Yes tems, RAID 5, RAID 50 the cluster. Volumes configured with Network RAID- Yes. 2 disks per RAID set can fail without 10 or greater on clustered storage sys- copying from another storage system in Yes tems, RAID 6 the cluster. Volumes configured with Network RAID10 or greater on clustered VSAs with virtual RAID Depends on the underlying RAID configuration of the storage system on which the VSA is installed. HP recommends configuring RAID 5 or RAID 6. Yes, if underlying storage system configured for RAID other than RAID 0. Mixing RAID configurations You may mix storage systems with different configurations of RAID within a cluster. This allows you to add new storage systems with different RAID levels. However, be certain to calculate the capacity of additional storage systems configured with the desired RAID level, because the cluster operates at the smallest usable per-storage system capacity. 58 Storage Configuration: Disk RAID and Disk Management