Netgear DGND3300v2 User Manual - Page 158
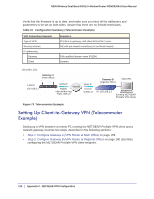
Setting Up Client-to-Gateway VPN (Telecommuter Example)
 |
View all Netgear DGND3300v2 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 158 highlights
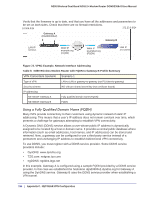
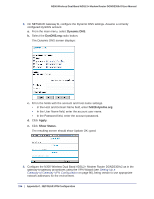
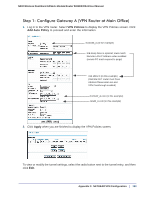
N300 Wireless Dual Band ADSL2+ Modem Router DGND3300v2 User Manual Verify that the firmware is up to date, and make sure you have all the addresses and parameters to be set on both sides. Assure that there are no firewall restrictions. Table 10. Configuration Summary (Telecommuter Example) VPN Consortium Scenario Type of VPN: Security scheme: IP addressing: Gateway Client Scenario 1 PC/client-to-gateway, with client behind NAT router IKE with pre-shared secret/key (not certificate based) Fully qualified domain name (FQDN) Dynamic 192.168.0.1/24 LAN IP 192.168.0.1 Gateway A (main office) WAN IP Internet FQDN ntgr.dyndns.org "from_GW_A" WAN IP 0.0.0.0 "toGW_A" Gateway B (regional office) Client PC IP: 192.168.2.3 (running NETGEAR ProSafe VPN client) Figure 73. Telecommuter Example Setting Up Client-to-Gateway VPN (Telecommuter Example) Setting up a VPN between a remote PC running the NETGEAR ProSafe VPN client and a network gateway involves two steps, described in the following sections: • Step 1: Configure Gateway A (VPN Router at Main Office) on page 159. • Step 2: Configure Gateway B (VPN Router at Regional Office) on page 160 describes configuring the NETGEAR ProSafe VPN client endpoint. 158 | Appendix C. NETGEAR VPN Configuration