Netgear DGND3300v2 User Manual - Page 90
Setting Up a Gateway-to-Gateway VPN Configuration, Table, Setting Up VPN Tunnels
 |
View all Netgear DGND3300v2 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 90 highlights
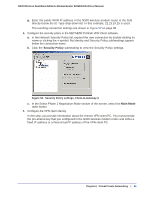
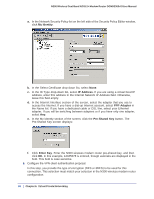
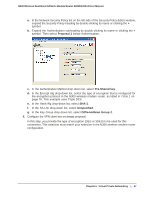
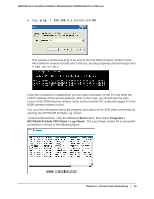
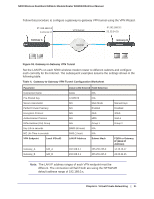
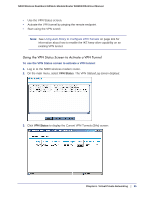
N300 Wireless Dual Band ADSL2+ Modem Router DGND3300v2 User Manual Note: Use the active VPN tunnel information and pings to determine whether a failed connection is due to the VPN tunnel or some reason outside the VPN tunnel. 9. The Connection Monitor screen for this connection is shown in the following figure: In this example you can see these settings: • The N300 wireless modem router has a GW address (public IP WAN address) of 22.23.24.25. • The N300 wireless modem router has a remote address (LAN IP address) of 192.168.3.1. • The VPN client PC has a local address (dynamically assigned address) of 192.168.2.2. While the connection is being established, the Connection Name field in this screen displays SA before the name of the connection. When the connection is successful, the SA changes to the yellow key symbol shown in the previous figure. Note: While your PC is connected to a remote LAN through a VPN, you might not have normal Internet access. If this is the case, you must close the VPN connection to have normal Internet access. Setting Up a Gateway-to-Gateway VPN Configuration Note: This section describes how to use the VPN Wizard to set up the VPN tunnel using the VPNC default parameters listed in Table 2 on page 79. If you have special requirements not covered by these VPNC-recommended parameters, see Setting Up VPN Tunnels in Special Circumstances on page 100 for information about how to set up the VPN tunnel. 90 | Chapter 6. Virtual Private Networking