D-Link DGS-3620-28TC-SI Product Manual - Page 256
BGP Confederation Settings, L3 Features > BGP > BGP Confederation Settings
 |
View all D-Link DGS-3620-28TC-SI manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 256 highlights
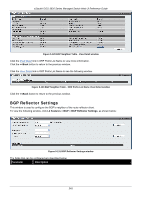
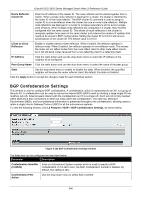
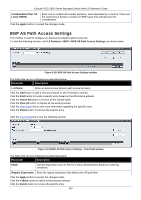
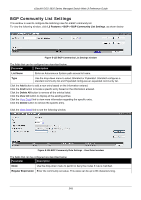
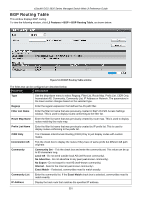
xStack® DGS-3620 Series Managed Switch Web UI Reference Guide Route Reflector Cluster ID Enter the IP address of the cluster ID. The route reflector and its clients together form a cluster. When a single route reflector is deployed in a cluster, the cluster is identified by the router ID of the route reflector. The BGP cluster ID command is used to assign a cluster ID to a route reflector when the cluster has one or more route reflectors. Multiple route reflectors are deployed in a cluster to increase redundancy and to avoid a single point of failure. When multiple route reflectors are configured in a cluster, they must be configured with the same cluster ID. This allows all route reflectors in the cluster to recognize updates from peers in the same cluster and reduces the number of updates that needs to be stored in BGP routing tables. Setting the cluster ID to 0.0.0.0 will remove specifications of the cluster ID. The default value is 0.0.0.0. Client to Client Reflection Enable or disable client-to-client reflection. When Enabled, the reflector operates in reflector mode. When Disabled, the reflector operates in non-reflector mode. This means the router will not reflect routes from the route reflect client to other route reflect clients, but it will still send routes received from a non-reflecting client to a reflecting client. IP Address Click the radio button and use the drop-down menu to select the IP address of the neighbor to be configured. Peer Group Name Click the radio button and use the drop-down menu to select the name of the peer group. State Use the drop-down menu to enable or disable the state. When Enabled, the specified neighbor will become the router reflector client. By default, this state is Disabled. Click the Apply button to accept the changes made for each individual section. BGP Confederation Settings This window is used to configure BGP confederation. A confederation, which is represented by an AS, is a group of the sub AS. A confederation can be used to reduce the internal BGP (iBGP) mesh by dividing a large single AS into multihop sub AS. External peers interact with the confederation as if it is a single AS. Each sub AS is fully meshed within itself and it has connections to other sub ASes within the confederation. The next hop, Multi Exit Discriminator (MED), and local preference information is preserved throughout the confederation, allowing users to retain a single Interior Gateway Protocol (IGP) for all the autonomous systems. To view the following window, click L3 Features > BGP > BGP Confederation Settings, as shown below: Figure 5-132 BGP Confederation Settings window The fields that can be configured are described below: Parameter Description Confederation Identifier (0-65535) Enter an Autonomous System number which is used to specify a BGP confederation. If it is set to zero, the BGP confederation number is deleted. By default, this setting is zero. Confederation Peer Action Use the drop-down menu to select Add or Delete. 246