Netgear WN203 User Manual - Page 75
Con Wireless Bridging, Apply, Wireless point-to-point bridge
 |
View all Netgear WN203 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 75 highlights
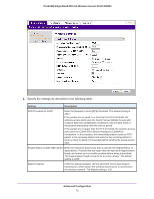
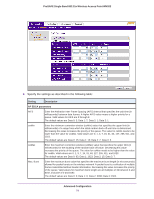
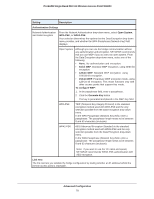
ProSAFE Single Band 802.11n Wireless Access Point WN203 Setting Description Station EDCA parameters AIFS Enter the Arbitration Inter-Frame Spacing (AIFS) interval that specifies the wait time (in milliseconds) between data frames. A higher AIFS value means a higher priority for a queue. Valid values for AIFS are 0 through 8. The default values are Data 0: 3; Data 1: 7; Data 2: 2; Data 3: 2. cwMin Enter the minimum contention window (cwMin) value that specifies the upper limit (in milliseconds) of a range from which the initial random back-off wait time is determined. Decreasing this value increases the priority of the queue. The value for cwMin needs to be lower than the value for cwMax. Valid values are 0, 1, 3, 7, 15, 31, 63, 127, 255, 511, and 1023. The default values are Data 0: 15; Data 1: 15; Data 2: 7; Data 3: 3. cwMax Enter the maximum contention window (cwMax) value that specifies the upper limit (in milliseconds) for the doubling of the random back-off value. Decreasing this value increases the priority of the queue. The value for cwMax needs to be higher than the value for cwMin. Valid values are 0, 1, 3, 7, 15, 31, 63, 127, 255, 511, and 1023. The default values are Data 0: 1023; Data 1: 1023; Data 2: 15; Data 3: 7. TXOP Limit Enter the transmission opportunity (TXOP) value that specifies the time interval (in microseconds) in which a client station can initiate transmissions on the wireless medium (WM). Decreasing this value increases the priority of the queue. Valid values for TXOP Limit are all multiples of 32 between 0 and 8192, inclusive of 0 and 8192. The default values are Data 0: 0; Data 1: 0; Data 2: 3008; Data 3: 1504. 3. Click the Apply button. Configure Wireless Bridging The wireless access point supports a wireless distributing system (WDS) that lets you build large bridged wireless networks. You can select from the following wireless access point modes: • Wireless point-to-point bridge. In this mode, the wireless access point can communicate with another access point that also functions in bridge mode. You can use this mode with or without client association. Whether or not you enable client association, use WEP, WPA-PSK, or WPA2-PSK to secure the communication. For information about how to configure this mode, see Configure a Point-to-Point Wireless Network on page 76. • Wireless point-to-multipoint bridge. In this mode, the wireless access point is the master for a group of up to four access points that function in bridge-mode. You can use point-to-multipoint bridge mode with or without client association. The other access points in the group need to be set to point-to-point bridge mode, using the MAC address of the master wireless access point. Rather than communicating directly with each other, all other bridge-mode access points send their traffic to the master wireless access point. Whether or not you enable client association, use WEP, WPA-PSK, or WPA2-PSK to secure the communication. For information about how to configure this mode, see Configure a Point-to-Multipoint Wireless Network on page 81. Advanced Configuration 75