Oki ML591 MICROLINE Reference Manual - Page 117
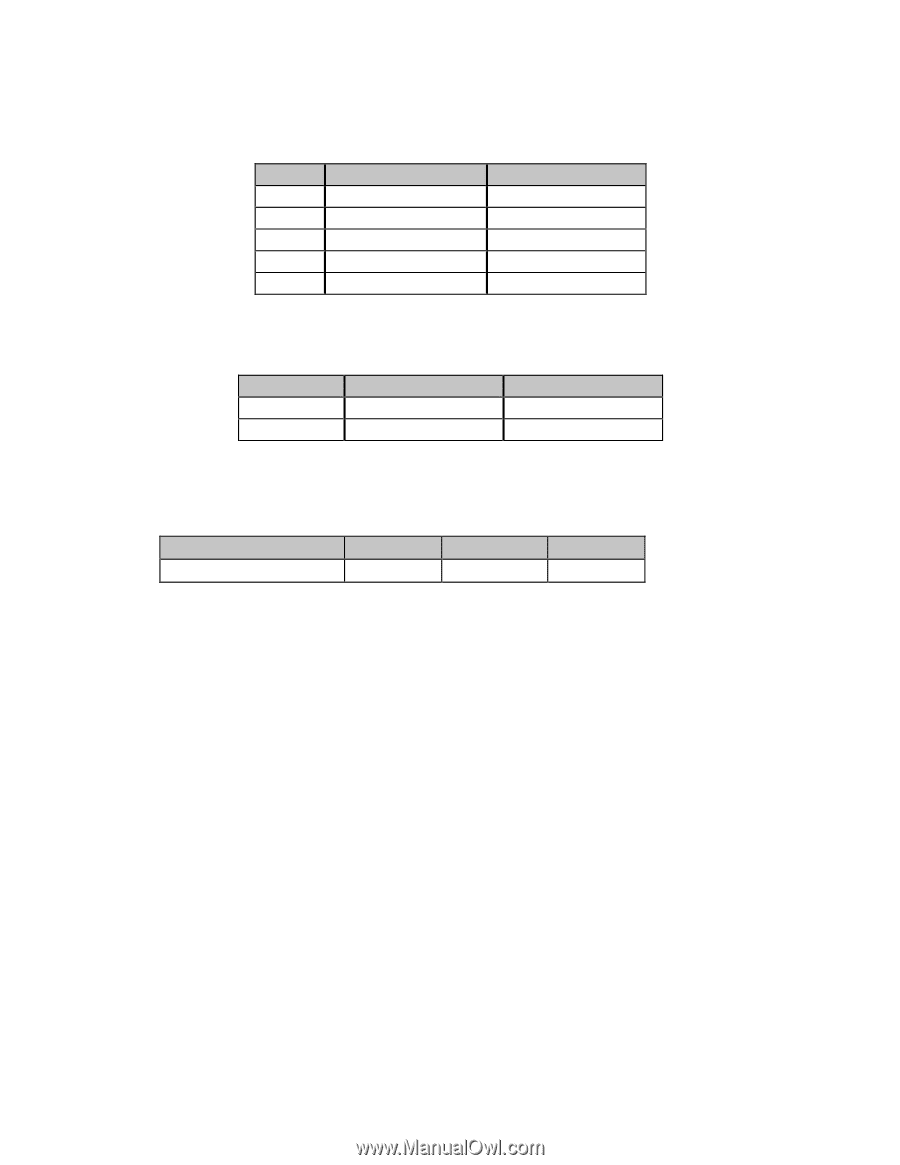
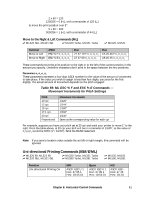
Table 57: IBM/E/ML ESC DLE @ Command, Maximum P, Values for 9-Pin Models
 |
View all Oki ML591 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 117 highlights
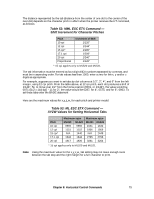
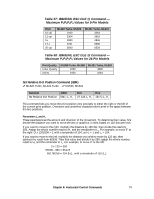
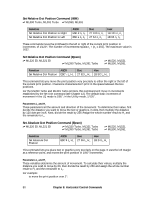
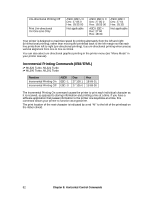
Table 57: IBM/E/ML ESC DLE @ Command - Maximum P1P2P3P4 Values for 9-Pin Models Pitch 10 cpi 12 cpi 15 17.1 20 cpi ML320 Turbo, ML520 1920 2304 2880 3291 3840 ML321 Turbo, ML521 3264 3916 4896 5595 6528 Table 58: IBM/E/ML ESC DLE @ Command - Maximum P1P2P3P4 Values for 24-Pin Models Print Quality Letter Quality Utility ML390 Turbo, ML590 2280 1920 ML391 Turbo, ML591 4896 3264 Set Relative Dot Position Command (IBM) ߜ ML320 Turbo, ML321 Turbo ߜ ML520, ML521 Function ASCII Dec Hex Set Relative Dot Position ESC | Ln Hn 27 124 Ln Hn 1B 7C Ln Hn This command lets you move the print position very precisely to either the right or the left of the current print position. Overscore and underline characters don't print in the space between the two positions. Parameters Ln and Hn These parameters set the amount and direction of the movement. To determine their value, first decide the distance you want to move the text or graphics, in dots, based on 120 dots per inch. If you want to move to the right, multiply the distance by 120 dpi, then divide the result by 256. Assign the whole number result to Hn and the remainder to Ln. For example, to move 3" to the right: (3 x 120)/256 = 1 with a remainder of 104, so Hn = 1 and Ln = 104. If you want to move to the left, multiply the distance you wish to move by 120 dpi, then subtract the result from 65536. Take that value and divide it by 256: assign the whole number result to Hn and the remainder to Ln. For example, to move 3" to the left: 3 x 120 = 360 65536 - 360 = 65176 65176/256 = 254 (Hn), with a remainder of 152 (Ln) Chapter 8: Horizontal Control Commands 79