TRENDnet TEW-829DRU Users Guide - Page 45
How to choose the type of wireless security, Wireless Security, Advanced Settings, Separate Clients
 |
View all TRENDnet TEW-829DRU manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 45 highlights
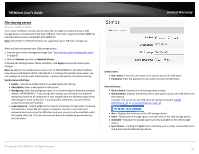
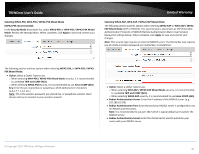
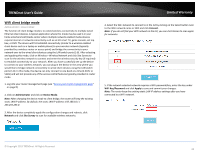
TRENDnet User's Guide Wireless Security - Allows you to configure the wireless encryption/security for the additional SSID. See the "How to choose the type of wireless security" and "Secure your wireless network" sections for details configuring wireless security. Advanced Settings o Separate Clients - By default, this option is left unchecked and allows all wireless client devices that are connected to the same wireless SSID to communicate with other wireless client devices. Checking this option will block communication between wireless client devices connecting with other wireless client devices. This feature is also known as L2 isolation or L2 client isolation. o WMM Mode - This feature enables Wi-Fi Multimedia QoS prioritization for wireless client devices that support WMM using the default priority level settings. Unchecking this option will disable WMM QoS on the additional SSID. Limited Warranty How to choose the type of wireless security Setting up wireless security is very important. Leaving your wireless network open and unsecure could expose your entire network and personal files to outsiders. TRENDnet recommends reading through this entire section and setting up wireless security on your new router. There are a few different wireless security types supported in wireless networking each having its own characteristics which may be more suitable for your wireless network taking into consideration compatibility, performance, as well as the security strength along with using older wireless networking hardware (also called legacy hardware). It is strongly recommended to enable wireless security to prevent unwanted users from accessing your network and network resources (personal documents, media, etc.). In general, it is recommended that you choose the security type with the highest strength and performance supported by the wireless computers and devices in your network. Please review the security types to determine which one you should use for your network. Wireless Encryption Types WPA: This encryption is significantly more robust than the older WEP legacy technology. Much of the older 802.11g hardware was been upgraded (with firmware/driver upgrades) to support this encryption standard. Total wireless speeds under this encryption type however are limited to 54Mbps. WPA/WPA2 Mixed Mode: This setting provides the router with the ability to detect wireless devices using either WPA or WPA2 encryption. Your wireless network will automatically change the encryption setting based on the first wireless device connected. For example, if the first wireless client that connects to your wireless network uses WPA encryption your wireless network will use WPA encryption. Only when all wireless clients disconnect to the network and a wireless client with WPA2 encryption connects your wireless network will then change to WPA2 encryption. Note: WPA2 encryption supports 802.11n speeds and WPA encryption will limit your connection speeds to 54Mbps WPA2: This is the most secure wireless encryption available today, similar to WPA encryption but more robust. This encryption standard also supports the highest connection speeds. If you find that one of your wireless network devices does not support WPA2 encryption, then set your router to either WPA or WPA-Auto encryption. There are two cipher types available which are Temporal Key Integrity Protocol (TKIP) and Advanced Encryption Standard (AES). AES should be used whenever possible to ensure the highest level of security. © Copyright 2019 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved. 38